Volume 14, Number 10—October 2008
Dispatch
New Hosts for Equine Herpesvirus 9
Figure 2
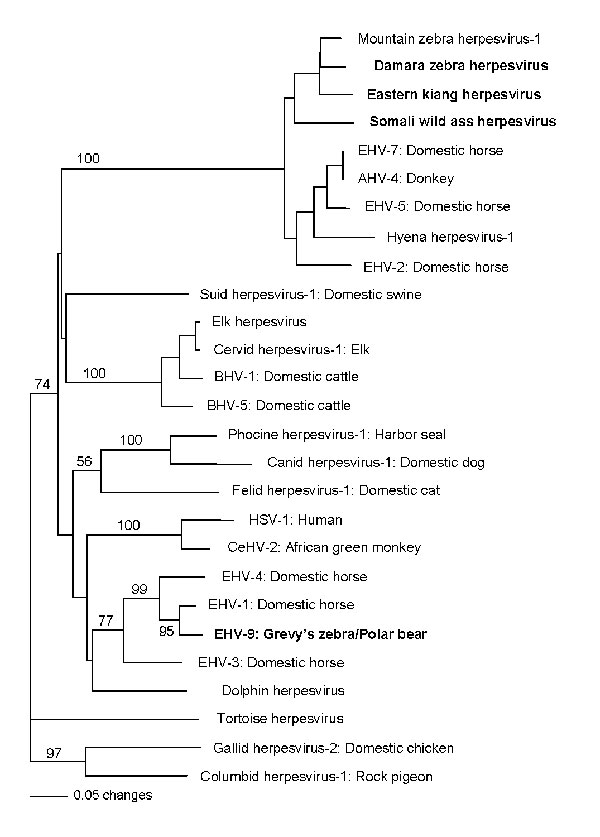
Figure 2. Phylogram of all equine herpesviruses and related viruses from other animals and their respective hosts created from a predicted amino acid segment of the DNA polymerase geneAll sequences obtained in this study are in boldface; bootstrap values >1,000 replicates are denotedNote clustering of equine gammaherpesviruses and paraphyletic grouping of equine herpesviruses (EHV) -1, EHV-4, and EHV-9 with primate herpesviruses and dolphin herpesvirusSequence accessions, sources, and abbreviations are as follows: mountain zebra (Equus zebra) herpesvirus AAS75147; Damara’s zebra (Eburchellii antiquorum) herpesvirus EU17155; eastern kiang (Ekiang holdereri) herpesvirus EU17156; Somali wild ass (Easinus somalicus) herpesvirus EU71754; EHV-7 from domestic horse (Ecaballus) ABW04888; asinine herpesvirus 4 (AHV-4) from donkey (Easinus) AAL14770; hyena (Crocuta crocuta) herpesvirus AB121852; EHV-2 from domestic horse ABS81334; suid herpesvirus 1 from domestic swine (Sus scrofa) DAA02153; elk (Cervus canadensis) herpesvirus ABC58213; cervid herpesvirus 1 from elk (Cervus canadensis) ABC58214; bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) from domestic cattle (Bos taurus) ABC58212; bovine herpesvirus 5 (BHV-5) from domestic cattle NP_954917; phocine herpesvirus 1 from Pacific harbor seal (Phoca vitulina richardsii); canid herpesvirus 1 from domestic dog (Canis lupus familiaris) ACB46532; felid herpesvirus 1 from domestic cat (Felis cattus domesticus) CAA12264; human herpesvirus 1 (HSV-1) from humans (Homo sapiens) AAL49731; cercopithecine herpesvirus 2 (CeHV-2) from African green monkey (Cercopithecus aethiops sabaeus) YP_164473; EHV-4 from domestic horse; EHV-1 from domestic horse BAG24215; EHV-9 from Grevy’s zebra (EGrevy’si), Persian onager (Ehemionus onager), and polar bear (Ursus maritimus) EU17146, EU17147, and EU17149; EHV-3 from domestic horse AF514779; and dolphin herpesvirus from bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatas) AAV1097The following 3 sequences were outgroups: tortoise herpesvirus from land tortoise (Testudo horsfieldii) ABC70838, gallid herpesvirus 2 from domestic chicken (Gallus domesticus) AAC55651, and columbid herpesvirus 1 from rock pigeon (Columba livia) ABP93390.