Volume 19, Number 9—September 2013
Research
Continued Evolution of West Nile Virus, Houston, Texas, USA, 2002–2012
Figure 3
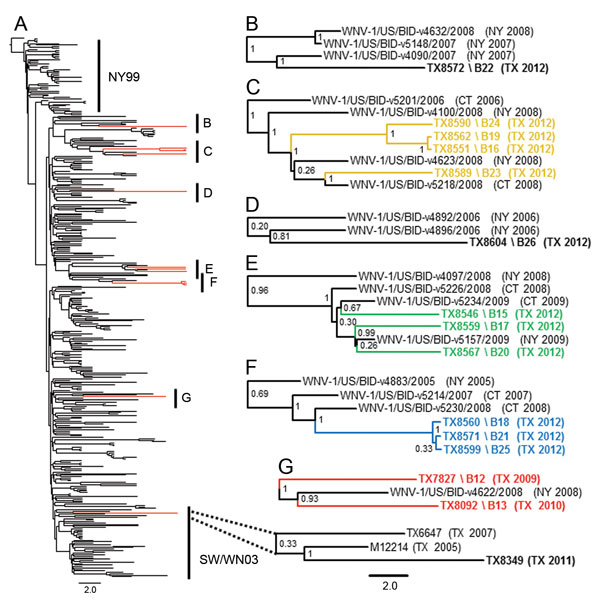
Figure 3. . Evolution of West Nile virus (WNV) in North America, 1999–2012. A) Bayesian coalescent tree of all published North American WNV isolates. The NY99 (NY99) and southwestern (SW/WN03) genotypes flank the North American (NA/WN02) genotype containing inferred monophyletic lineages B–G of the novel 2010–2012 Harris County, Texas, WNV isolates. Red indicates WNV isolates sequenced in this study. Isolates sequenced in this study are indicated in boldface. B) TX8572 2012 Harris County isolate. D) TX8604 2012 Harris County isolate. C and E–G) Proposed monophyletic groups 7–10 described in Figure 1: C) group 10 (yellow); E) group 9 (green); F) group 8 (blue); G) group 7 (red). Dotted lines indicate distribution of the 2011 TX8349 isolate in the SW/WN03 genotype. Posterior probabilities (range 0.00–1.00) are indicated along branches to provide statistical support for inferred topologies. Scale bars indicate divergence time in years.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.