Volume 20, Number 4—April 2014
Research
Regional Variation in Travel-related Illness acquired in Africa, March 1997–May 2011
Figure 2
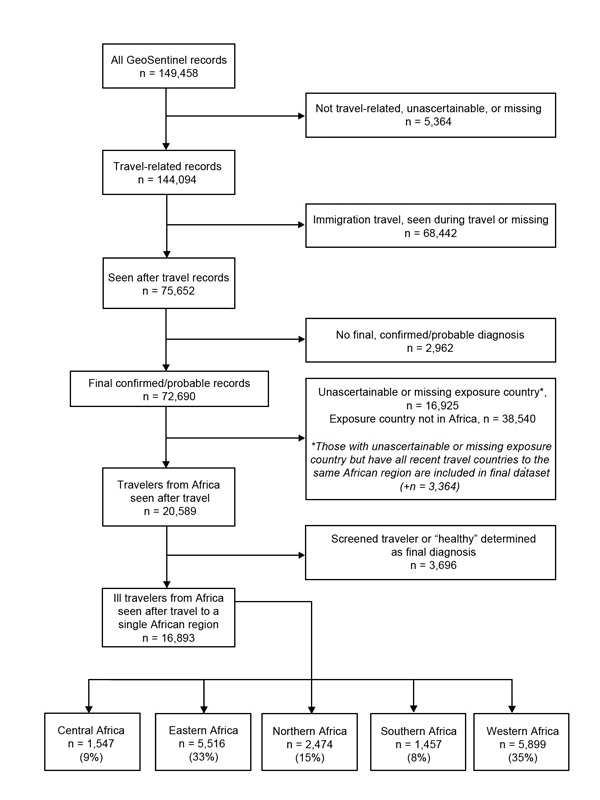
Figure 2. . . Flowchart for analysis of ill returned travelers from Africa reported in the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network, March 1997–May 2011. The United Nations geoscheme was used to classify Africa into subregions (5).
References
- World Tourism Organisation. UNWTO tourism highlights 2012 edition [cited 2013 Jan 8]. http://mkt.unwto.org/en/publication/unwto-tourism-highlights-2012-edition
- Freedman DO, Weld LH, Kozarsky PE, Fisk T, Robins R, von Sonnenburg F, Centron; GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Spectrum of disease and relation to place of exposure among ill returned travelers. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:119–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jensenius M, Davis X, von Sonnenburg F, Schwartz E, Keystone JS, Leder K, GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Multicenter GeoSentinel analysis of rickettsial diseases in international travelers, 1996–2008. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1791–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mendelson M, Davis XM, Jensenius M, Keystone JS, von Sonnenburg F, Hale DC, GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Health risks for travelers to South Africa: the GeoSentinel experience and implications for the 2010 FIFA World Cup. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;82:991–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- United Nations Statistics Division. Africa geoscheme [cited 2012 May 10]. http://millenniumindicators.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm
- Checkley AM, Smith A, Smith V, Blaze M, Bradley D, Chiodini PL, Risk factors for mortality from imported falciparum malaria in the United Kingdom over 20 years: an observational study. BMJ. 2012;344:e2116. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sabatinelli G, Ejov M, Joergensen P. Malaria in the WHO European Region (1971–1999). Euro Surveill. 2001;6:61–5 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nicolls DJ, Weld LH, Schwarz E, Reed C, von Sonnenburg F, Freedman DO, for the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Characteristics of schistosomiasis in travelers reported to the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network, 1997–2008. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79:729–34 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Leder K, Tong S, Weld L, Kain KC, Wilder-Smith A, von Sonnenburg F, for the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Illness in travelers visiting friends and relatives: a review of the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:1185–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hay SI, Rogers DJ, Toomer JF, Snow RW. Annual Plasmodium falciparum entomological inoculation rates (EIR) across Africa: literature survey, internet access and review. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2000;94:113–27 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hamer DH, Connor BA. Travel health knowledge, attitudes and practices among United States travelers. J Travel Med. 2004;11:23–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wilder-Smith A, Kahirullah NS, Song JH, Chen CY, Torresi J. Travel health knowledge, attitudes and practices among Australasian travelers. J Travel Med. 2004;11:9–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lopez-Velez R, Bayas JM. Spanish travelers to high-risk areas in the tropics: airport survey of travel health knowledge, attitudes and practices in vaccination and malaria prevention. J Travel Med. 2007;14:297–305 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gautret P, Ribadeau-Dumas F, Parola P, Brouqui P, Bourhy H. Risk for rabies importation from North Africa [review]. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:2187–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- United Nations. UNAIDS 2011 World AIDS Day report, fact sheet [cited 2012 May 10]. http://www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/factsheet/2011/20111121_FS_WAD2011_global_en.pdf
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis control 2011 [cited 2012 May 10]. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/
- Matteelli A, Carosi G. Sexually transmitted diseases in travelers. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1063–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matteelli A, Schlagenhauf P, Carvalho AC, Weld L, Davis XM, Wilder-Smith A, for the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Travel-associated sexually transmitted infections: an observational cross-sectional study of the GeoSentinel surveillance database. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:205–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hagmann S, Neugebauer R, Schwartz E, Perret C, Castelli F, Barnett ED, for the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network. Illness in children after international travel: analysis from the GeoSentinel Travel Surveillance Network. Pediatrics. 2010;125:e1072–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bottieau E, Clerinx J, Schrooten W, Van den Enden E, Wouters R, Van Esbroek M, Etiology and outcome of fever after a stay in the tropics. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1642–8 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herbinger KH, Drerup L, Alberer M, Norhdurft HD, von Sonnenburg F, Loscher T. Spectrum of imported infectious diseases among children and adolescents returning from the tropics and subtropics. J Travel Med. 2012;19:150–7 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reisinger Y, Mavondo F. Travel anxiety and intentions to travel internationally: implications of travel risk perception. J Travel Res. 2005;43:212–5. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Schwartz E, Meltzer E, Mendelson M, Tooke A, Steiner F, Gautret P. Detection on four continents of dengue fever cases related to an ongoing outbreak in Luanda, Angola, March to May 2013. Euro Surveill. 2013;18: .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Njeru I. Dengue/DHF Update (33): Asia, Africa, Pacific. ProMed. 2013 Apr 28. [cited 2013 May1] http://www.promedmail.org, archive no. 20130428.1676860
1Contributing members of the GeoSentinel Surveillance Network are listed at the end of this article.
Page created: March 12, 2014
Page updated: March 12, 2014
Page reviewed: March 12, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.