Volume 20, Number 7—July 2014
Dispatch
New Viruses in Idiopathic Human Diarrhea Cases, the Netherlands
Figure 2
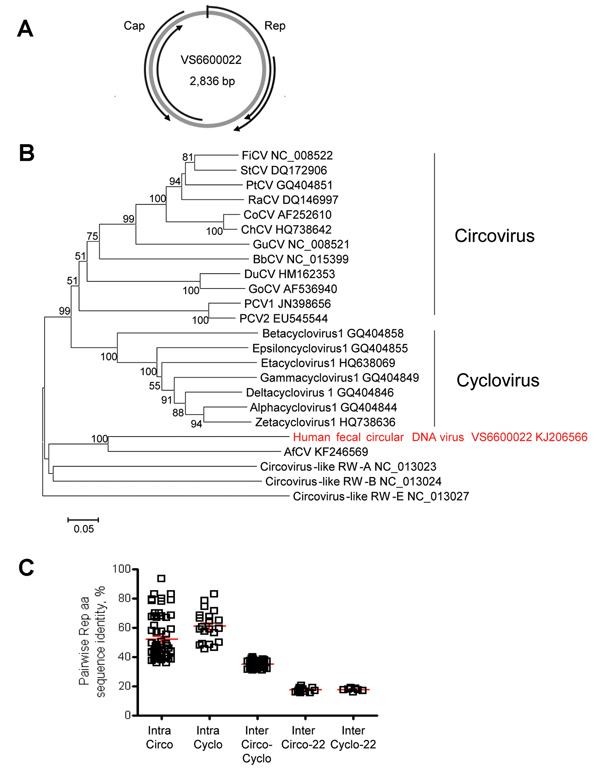
Figure 2. Genome organization and phylogenetic analysis of human fecal circular DNA virus VS6600022, the Netherlands, 2005–2009A) Putative schematic genome organizationArrows indicate major open reading framesCap, capsid; Rep, rolling circle replication initiator proteinB) Phylogenetic neighbor-joining tree with p-distances and 1,000 bootstrap replicates created with MEGA5 of amino acid sequences of the Rep genes of human fecal circular DNA virus VS6600022 and representative circoviruses that were aligned by using ClustalX2.0 (http://www.clustal.org/)Virus isolated in this study is indicated in redScale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per siteFiCV, finch circovirus; StCV, starling circovirus; PtCV, Pan troglodytes circovirus; RaCV, raven circovirus; CoCV, columbid circovirus; ChCV, chicken circovirus; GuCV, gull circovirus; PCV, porcine circovirus; BbCV; Barbus barbus circovirus; DuCV, duck circovirus; GoCV, goose circovirus; AfCV, Arctocephalus forsteri circovirusC) Pairwise intraspecies (Intra) and interspecies (Inter) amino acid sequence identities determined by using Bioedit 7.0.9.0 (http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html) between the Rep protein sequences of VS6600022 and representative species in the genera Circovirus (Circo) and Cyclovirus (Cyclo)Each square represents the pairwise RdRP amino acid sequence identity between the viruses in panel BRed bars indicate mean and SEM.