Confirmed Bacillus anthracis Infection among Persons Who Inject Drugs, Scotland, 2009–2010
Malcolm Booth
1, Lindsay Donaldson
1, Xizhong Cui, Junfeng Sun, Stephen Cole, Susan Dailsey, Andrew Hart, Neil Johns, Paul McConnell, Tina McLennan, Benjamin Parcell, Henry Robb, Benjamin Shippey, Malcolm Sim, Charles Wallis, and Peter Q. Eichacker
Author affiliations: Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow, Scotland, UK (M. Booth, L. Donaldson, A. Hart); National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA (X. Cui, J. Sun, P.Q. Eichacker); Ninewells Hospital, Dundee, Scotland, UK (S. Cole, B. Parcell); Victoria Infirmary, Glasgow (S. Dailsey); Queen Margaret and Victoria Hospitals, Dumfermline, Scotland, UK (N. Johns, B. Shippey); Crosshouse Hospital, Kilmarnock, Scotland, UK (P. McConnell); Hairmyres Hospital, East Kilbride, Scotland, UK (T. McLennan); Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert, Scotland, UK (H. Robb); Western Infirmary, Glasgow (M. Sim); Western General Hospital, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK (C. Wallis)
Main Article
Figure 4
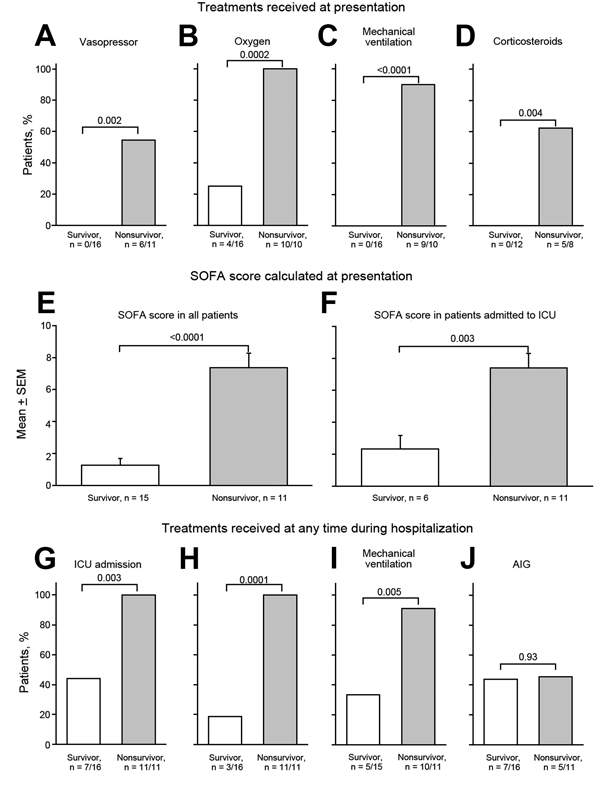
Figure 4. Treatments at time patients sought care, SOFA scores, and treatments anytime during hospitalization of persons who inject drugs and were part of an outbreak of Bacillus anthracis infection, Scotland, UK, 2009–2010. Included are the 27 patients for whom data were available on treatment with vasopressors (A), oxygen therapy (B), mechanical ventilation (C), or steroids (D); the mean (+ SEM) SOFA score calculated within the first 24 h of hospitalization in all patients (E) and in only those who required ICU admission (F); and the proportion of patients at time they sought care who required ICU admission (G) or were treated with vasopressors (H), mechanical ventilation (I), or anthrax immune globulin (J) at any time during hospitalization. For panels A–D and G–J, n = the number of survivors or nonsurvivors receiving treatment/total number for whom data were available. For panels E and F, n = the number of survivors or nonsurvivors for whom SOFA scores were calculated. SOFA, sequential organ failure assessment; ICU, intensive care unit.
Main Article
Page created: August 15, 2014
Page updated: August 15, 2014
Page reviewed: August 15, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
