Volume 21, Number 1—January 2015
Dispatch
Enzootic Transmission of Yellow Fever Virus, Venezuela
Figure 1
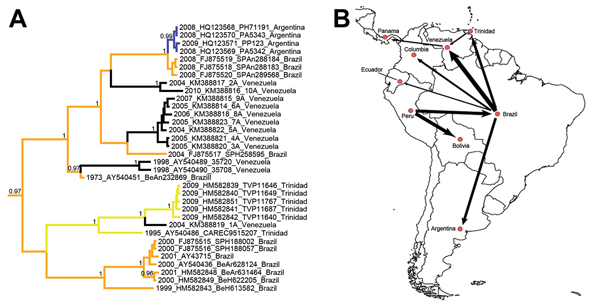
Figure 1. A) Bayesian maximum clade credibility (MCC) tree for YFV in the Americas based on 654 nt of the prM/E fragment. Taxon labels include year of isolation, GenBank accession number, strain designation, and country of isolation. Terminal branches of the tree are colored according to the sampled location of the taxon at the tip. Internal branches are colored according to the most probable (modal) location of their parental nodes. Nodes with posterior probabilities (clade credibilities) >0.95 are labeled accordingly in black. Scale bar indicates time in years. B) Magnified inset of the MCC phylogeny showing the tree topology for a subset of South American genotype I strains. C) Bayes factor (BF) test for significant non-zero rates indicating the statistical support for epidemiologically linked countries. Rates supported by a BF >5 are shown. The thickness of the arrows represents the relative strength by which the rates are supported. The Technical Appendix presents the details of the 124 sequences used in this study