Volume 21, Number 4—April 2015
Research
Population Structure and Antimicrobial Resistance of Invasive Serotype IV Group B Streptococcus, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Figure 1
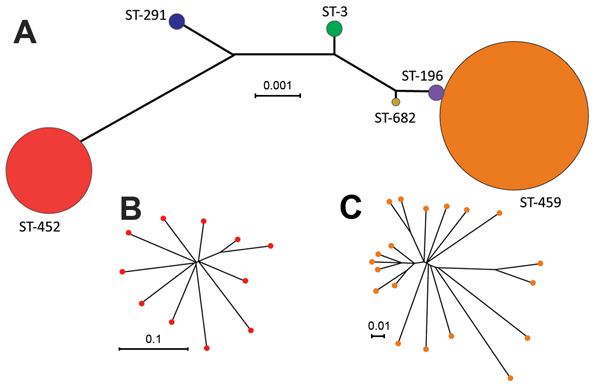
Figure 1. Inferred genetic relationships of invasive serotype IV group B Streptococcus (GBS), Toronto, Ontario, Canada. A) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree constructed by using the concatenated sequences of the 7 gene loci (sdhA, adhP, tkt, glcK, atr, pheS, and glnA) used in the multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme for GBS. Each circle represents a single MLST sequence type (ST); circle colors differentiate the 6 STs found among strains in our collection and their sizes are proportional to the number of isolates. B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis based on concatenated sequences of 316 nonredundant single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci identified by whole-genome sequencing relative to the core genome ST-452 reference strain NGBS572, which shows further diversity within ST-452. C) Diversity within ST-459 serotype IV GBS shown by neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis based on concatenated sequences of 526 nonredundant SNP loci relative to the core genome of ST-459 reference strain NGBS061. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.