Volume 21, Number 6—June 2015
Research
Cost-effectiveness of Chlamydia Vaccination Programs for Young Women
Figure 1
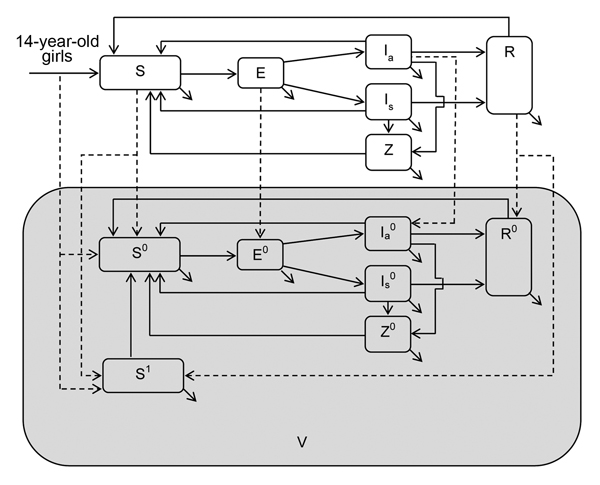
Figure 1. Schematic for exploring the cost-effectiveness of the hypothetical chlamydia vaccine. S, susceptible; E, exposed; Ia, infectious asymptomatic; Is, infectious symptomatic; R, infection-conferred immunity; Z, sequelae; V (shaded area), vaccinated; superscripts, none, not vaccinated; 0, vaccinated but not effective; 1, vaccinated and effective. Infected persons move into the exposed (E, incubation compartment). From E, they move to either the infectious asymptomatic (Ia) or infectious symptomatic (Is) compartment on the basis of the probability of being symptomatic and the duration of incubation. Infected persons may recover naturally and move to the infection-conferred immunity compartment R, receive treatment, and move back to the susceptible compartment S or show development of chlamydia-associated complications and enter the sequelae compartment Z. Vaccinated persons enter the super compartment V and those whose vaccination was not effective continue to move through the health status compartment (S0, E0, Ia0, Is0, Z0, R0) states similar to those not vaccinated (S, E, Ia, Is, Z, R) because we assumed that there was no prophylactic benefit for that group. Conversely, persons with effective vaccination are not susceptible (S1). They stay immune for a specified time on the basis of the duration of the vaccine-conferred immunity applied, after which they move to the vaccinated but not effective compartment (S0). No vaccination was applied to persons in the infectious symptomatic and sequelae compartments. Also, the vaccine was assumed to be ineffective for persons in the exposed (E) and infectious asymptomatic (Ia) compartments. Because we assumed that sexual debut (first sexual intercourse) is at the age of 15 years, 14-year-old girls enter the susceptible compartments (S, S0, and S1) on the basis of vaccination coverage and vaccine efficacy values applied.