Volume 22, Number 10—October 2016
Research
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Doxycycline Efficacy for Rectal Lymphogranuloma Venereum in Men Who Have Sex with Men
Figure 2
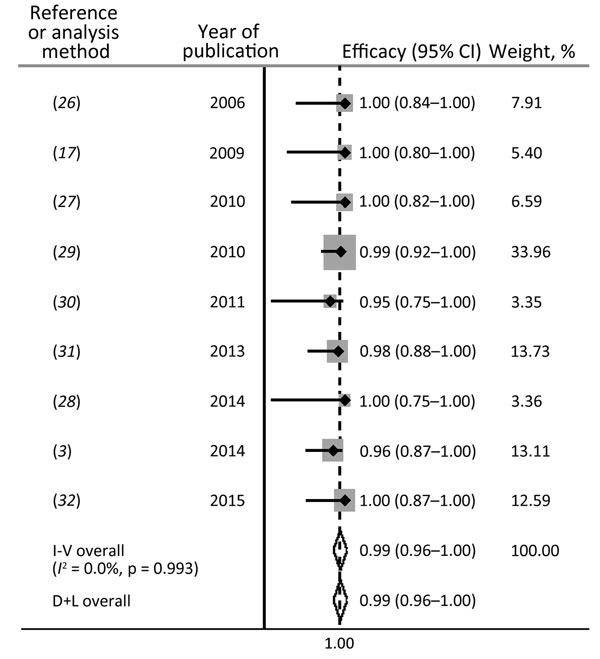
Figure 2. Efficacy of doxycycline (100 mg 2×/d for 21 d) for treatment of rectal lymphogranuloma venereum infection in men who have sex with men. I-V, inverse-variance (fixed) method; D+L, DerSimonian and Laird (random-effects) method; I2, test for heterogeneity.
Page created: September 20, 2016
Page updated: September 20, 2016
Page reviewed: September 20, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.