Volume 22, Number 4—April 2016
Letter
Sustained Elevated Cytokine Levels during Recovery Phase of Mayaro Virus Infection
Figure
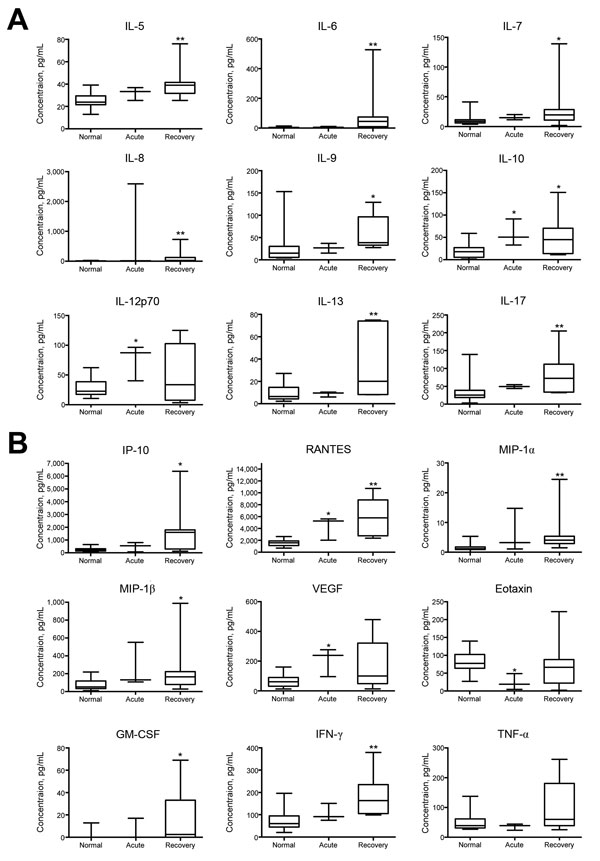
Figure. Changes in cytokine and growth factor levels in the acute and recovery phase of Mayaro fever. Box-and-whisker plots show median, upper and lower quartile, minimum, and maximum values. A) During the prolonged recovery phase, serum levels of interleukin (IL) 5–10, IL-13, and IL-17 were significantly elevated compared with levels for healthy controls. IL-10 levels were also significantly increased during the acute phase, as were IL-12p70 levels. B) Significantly increased serum concentrations of interferon-γ (IFN-γ)–induced protein 10 (IP-10), regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), macrophage inflammatory proteins (MIP)–1α and –1β, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and IFN-γ were detected in the prolonged recovery phase; significant elevations were also seen in the acute phase for RANTES and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) concentrations showed a nonsignificant median decrease during the acute phase, whereas eotaxin levels were significantly decreased at that time. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01, versus values for healthy controls (Kruskal-Wallis test).