Volume 22, Number 5—May 2016
Research
Differences in Genotype, Clinical Features, and Inflammatory Potential of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto Strains from Europe and the United States
Figure 3
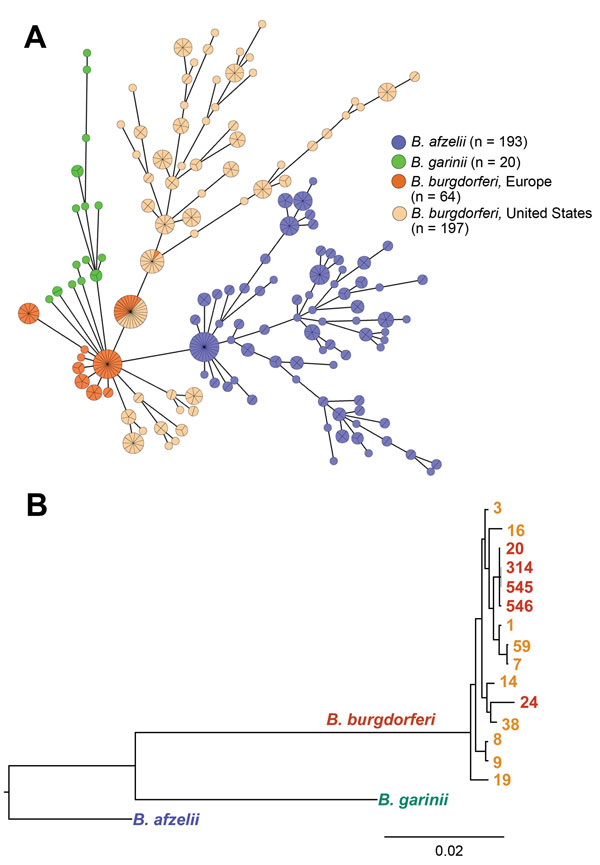
Figure 3. Phylogenetic comparison of 3 major pathogenic Borrelia species (Borrelia afzelii, B. garinii, and B. burgdorferi sensu stricto) that cause Lyme borreliosis. A) Minimum spanning tree analysis of 474 B. burgdorferi sensu lato human isolates. Analysis included 404 previously published datasets available in the multilocus sequence typing database (http://pubmlst.org/borrelia/) as of May 5, 2015, and 70 B. burgdorferi sensu stricto isolates from this study. Circles and numbers indicate specific sequence types (STs). Sizes of circles indicate MLST sample size and colors indicate origin of isolates. Lengths of lines connecting STs indicate order of certainty. STs connected by the shortest line are single locus-variants. B) Bayesian consensus tree resulting from simultaneous analysis of concatenated sequences of housekeeping genes of 70 B. burgdorferi sensu stricto isolates included in this study, representative strains of B. afzelii (http://pubmlst.org/borrelia/id:1546), and B. garinii (http://pubmlst.org/ borrelia/id:1829). Values at nodes indicate Bayesian posterior probabilities (proportion of sampled trees containing the taxon bipartition). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.