Volume 22, Number 7—July 2016
Letter
Use of Plasma Therapy for Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Encephalopathy
Figure
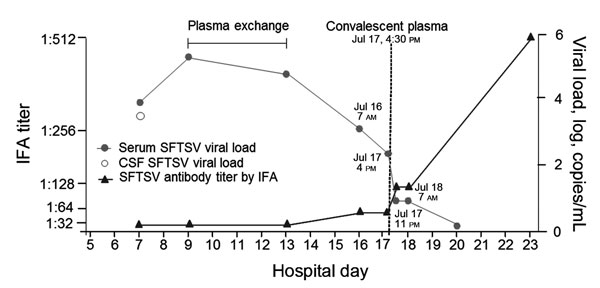
Figure. Changes in viral RNA load and immunofluorescence antibody titer and timing of therapies for a 62-year-old woman with SFTSV-associated encephalopathy in response to plasma exchange followed by convalescent plasma therapy, South Korea, 2015. CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; IFA, indirect immunofluorescence antibody assay; SFTSV, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: June 14, 2016
Page updated: June 14, 2016
Page reviewed: June 14, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.