Volume 22, Number 8—August 2016
Synopsis
Co-infections in Visceral Pentastomiasis, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Figure 1
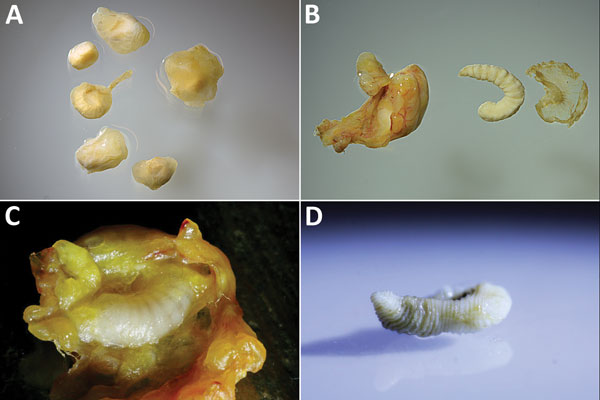
Figure 1. Resected cystic pentastomid lesions extracted from patients during abdominal surgery, Sankuru District, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2014–2015. A) Six abdominal cysts resected from patient 3, who was found to be co-infected: 3 cysts each were Armillifer grandis and A. armillatus larvae, as determined by PCR. B) One of 2 resected A. armillatus cysts from patient 5. The fibrous capsule, the larva itself, and the parasite’s exuvia are shown. The larva has 20 annulations, morphologically consistent with the molecular result of A. armillatus. C) Resected and opened cyst from patient 5. The A. armillatus larva (as determined by PCR) is still embedded in its capsule. D) A. grandis larva from patient 2 with >25 annulations.
Page created: July 15, 2016
Page updated: July 15, 2016
Page reviewed: July 15, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.