Azithromycin Resistance and Decreased Ceftriaxone Susceptibility in Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Hawaii, USA
John Papp, A. Jeanine Abrams, Evelyn Nash, Alan R. Katz, Robert D. Kirkcaldy, Norman P. O’Connor, Pamela S. O’Brien, Derek H. Harauchi, Eloisa V. Maningas, Olusegun O. Soge, Ellen N. Kersh, Alan Komeya, Juval E. Tomas, Glenn M. Wasserman, Gail Y. Kunimoto, David L. Trees, and A. Christian Whelen
Author affiliations: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (J.R. Papp, A.J. Abrams, E. Nash, R.D. Kirkcaldy, E.N. Kersh, D.L. Trees); University of Hawaii, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA (A.R. Katz, A. Komeya, J.E. Tomas, G.M. Wasserman, A.C. Whelen); Hawaii Department of Health, Honolulu (A.R. Katz, G.M. Wasserman, N.P. O’Connor, P.S. O’Brien, D.H. Harauchi, E.V. Maningas, G.Y. Kunimoto, A.C. Whelen); Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project Regional Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA (O.O. Soge)
Main Article
Figure
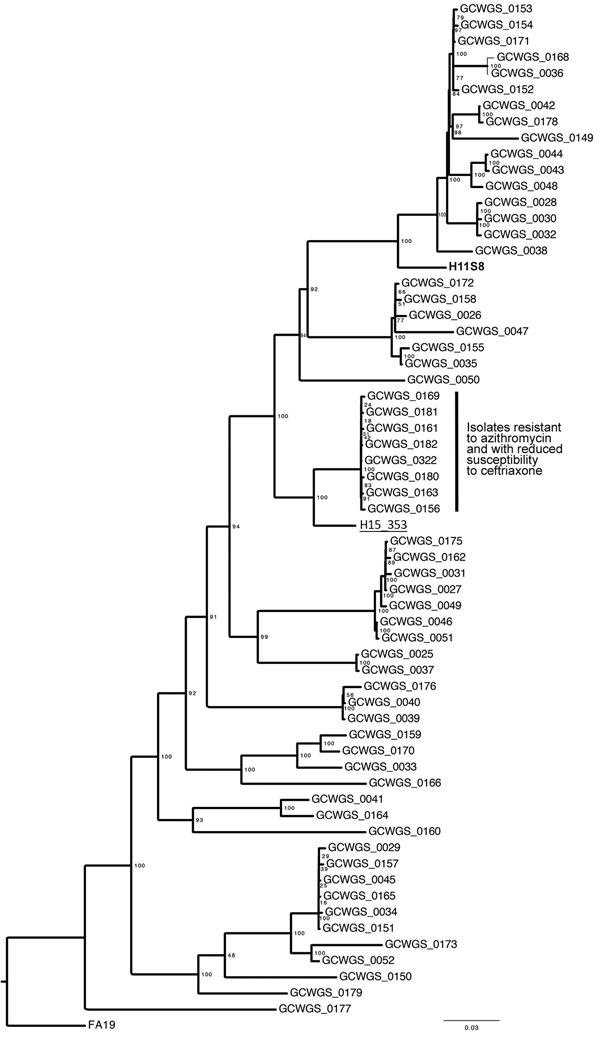
Figure. Maximum-likelihood phylogeny of Neisseria gonorrhoeae samples (N = 62) collected in Hawaii during February–May 2016, 1 isolate collected in Hawaii in 2011, and 1 isolate collected in the United Kingdom in 2015. The clade denoted with the black vertical bar contains 8 samples that exhibited resistance to azithromycin (MIC >256 µg/mL by Etest) and reduced susceptibility to ceftriaxone (MIC range 0.094–0.125 µg/mL). The 2011 isolate from Hawaii (H11S8, bold) also exhibited resistance to azithromycin. The United Kingdom isolate (underlined) was associated with failed dual antimicrobial therapy of ceftriaxone and azithromycin. The phylogeny is based on the core genome single nucleotide polymorphism alignment of the 62 genomes and the FA19 reference genome. Values on the nodes of the phylogeny (based on 1,000 bootstrap replicates) represent the support for each node and the corresponding clade. Scale bar indicates substitutions per site.
Main Article
Page created: April 17, 2017
Page updated: April 17, 2017
Page reviewed: April 17, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
