Volume 24, Number 11—November 2018
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Rickettsia typhi as Cause of Fatal Encephalitic Typhus in Hospitalized Patients, Hamburg, Germany, 1940–1944
Figure 2
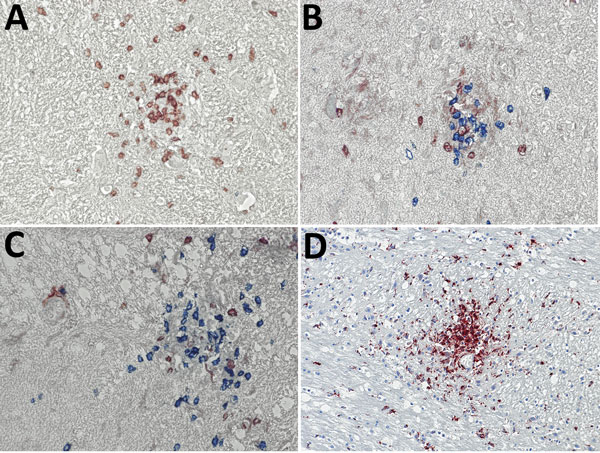
Figure 2. Immunohistochemical analyses of nodule cell compositions from typhus patients during World War II, Hamburg, Germany, 1940–1944. Tissue sections were incubated with specific antibodies and visualized with immunoperoxidase (brown) or immunophosphatase (blue) stains and lightly counterstained with hematoxylin. A) CD3 stain (brown) for T cells and CD20 stain (blue) for B cells. Only T cells are visible within the nodule. Original magnification ×40. B, C) CD4 stain (brown) and CD8 stain (blue) for T cell subsets. The nodules consist of a mixture of both cell types, with a predominance of CD8-positive cytotoxic T cells. Original magnifications ×40. D) CD68 stain (brown) for macrophages and microglia. A strong positivity is seen in the nodules and staining is also scattered in the surrounding brain parenchyma. Original magnification ×20.