Volume 24, Number 5—May 2018
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Two Cases of Israeli Spotted Fever with Purpura Fulminans, Sharon District, Israel
Introduction

In support of improving patient care, this activity has been planned and implemented by Medscape, LLC and Emerging Infectious Diseases. Medscape, LLC is jointly accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), to provide continuing education for the healthcare team.
Medscape, LLC designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.00 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
All other clinicians completing this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. To participate in this journal CME activity: (1) review the learning objectives and author disclosures; (2) study the education content; (3) take the post-test with a 75% minimum passing score and complete the evaluation at http://www.medscape.org/journal/eid; and (4) view/print certificate.
Release date: April 12, 2018; Expiration date: April 12, 2019
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to:
1. Assess different subspecies of Rickettsia conorii in terms of their virulence
2. Evaluate common presenting symptoms and signs of Israel spotted fever
3. Analyze different laboratory findings in the current case series of Israel spotted fever
CME Editor
Thomas J. Gryczan, MS, Technical Writer/Editor, Emerging Infectious Diseases. Disclosure: Thomas J. Gryczan, MS, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
CME Author
Charles P. Vega, MD, FAAFP, Health Sciences Clinical Professor, University of California, Irvine, Department of Family Medicine; Associate Dean for Diversity and Inclusion, University of California, Irvine, School of Medicine; Executive Director, University of California, Irvine, Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community, Irvine, California. Disclosure: Charles P. Vega, MD, FAAFP, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: served as an advisor or consultant for Johnson & Johnson Healthcare; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Shire Pharmaceuticals.
Authors
Disclosures: Regev Cohen, MD; Frida Babushkin, MD; Maurice Shapiro, MD; Martina Uda, MD; Yafit Atiya-Nasagi, PhD; Dar Klein, MSc; and Talya Finn, MBBS, have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Abstract
We report a series of 5 case-patients who had Israeli spotted fever, of whom 2 had purpura fulminans and died. Four case-patients were given a diagnosis on the basis of PCR of skin biopsy specimens 3–4 days after treatment with doxycycline; 1 case-patient was given a diagnosis on the basis of seroconversion. Rickettsia spp. from the 2 case-patients who died were sequenced and identified as Rickettsia conorii subsp. israelensis. Purpura fulminans has been described in association with R. rickettsii and R. indica, but rarely with R. conorii subsp. israelensis.
Rickettsia conorii is the etiologic agent of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF), which is considered one of the most severe and life-threatening rickettsial infections. Among the 4 strains of R. conorii (R. conorii subsp. conorii, R. conorii subsp. caspia, R. conorii subsp. indica, and R. conorii subsp. israelensis), R. conorii subsp. israelensis, which causes Israeli spotted fever (ISF), is believed to be the most virulent strain and shows a case-fatality rate of up to 32.3% in hospitalized patients (1). R. conorii is endemic to Israel (2). However, in recent years, Rickettsia spp. other than R. conorii have been identified and reported from Israel, including R. africae, R. massiliae, R. sibirica (3,4).
Within the R. conorii group, there are clinical and virulence differences. For example, infections with R. conorii subsp. israelensis have higher case-fatality rates than infections with the R. conorii Malish strain (29% vs. 13%), and R. conorii subsp. israelensis is rarely is associated with an eschar at the site of a tick bite (5,6). ISF has also been reported from other Mediterranean countries, including Portugal (7), Italy and Sicily (6), and Tunisia (8). R. conorii subsp. conorii that cause MSF are also endemic to Europe, Asia, and Africa.
ISF usually manifests as fever with a maculopapular rash, usually involving the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. Patients who die from ISF typically have multiorgan failure, acute renal or hepatic failure, and acute encephalitis; all are attributed to the affinity of the Rickettsia spp. to endothelial cells with resultant vasculitis. The typical maculopapular rash might transform to become hemorrhagic with discrete purpurial lesions, but true manifestation of ISF purpura fulminans is not frequently reported in Israel or from other countries.
Because serologic cross-reactivity occurs across the spotted fever group (SFG) rickettsiae (9) and the primary means of diagnosis is through serum antibody assays, accurate distinction between different subspecies requires identification of the actual infecting bacterium. This cross-reactivity, overlap in geographic distributions, and the different clinical severities highlight the need to better differentiate between these rickettsial species. A correct diagnosis is critical for predicting the pathologic complications that would arise because of infection (10).
We report a case series of 5 patients with ISF from the same geographic area (Sharon District in Israel) (Tables 1, 2). Four of these case-patients were detected during April–May 2017. Two case-patients had purpura fulminans and both died. These cases were a part of a national outbreak of SFG rickettsiosis.
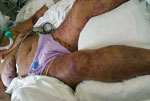
A 75-year-old woman with a history of hypertension, a tourist from Ukraine who had been staying with her daughter in Netanya for the previous 3 months, came to an emergency department in October 2016 with 6 days of fever, weakness, and anorexia. She had been exposed to 3 dogs at the house of her daughter but had no recollection of tick exposure. At admission, she was coherent but in a state of septic shock; she was hypotensive and had a disseminated, fern-leaf pattern, purpural rash over her body, including the face (Figure 1). Laboratory findings included leukocytosis, severe thrombocytopenia (23,000 platelets/μL), hyponatremia (sodium level 126 mmol/L), acute renal failure, increased levels of liver enzymes and creatine kinase (CK), and disseminated intravascular coagulation (Table 1).
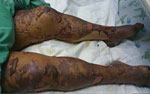
She was admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) and given broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug therapy, including intravenous doxycycline. During the next 2 days, multiorgan failure, severe jaundice, liver failure, and acute lung injury developed, and the rash became bullous with clear serous fluid (Figure 2). A skin biopsy specimen from a hemorrhagic lesion was obtained and tested by PCR. The result was positive for R. conorii subsp. israelensis. Serologic analysis for rickettsia at the time of admission (day 9 after disease onset) showed no reactivity, but another sample obtained 10 days later was positive (IgG titer 1:800) for SFG rickettsiae.
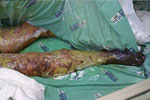
The skin lesions became dusky, necrosis appeared at the extremities (Figure 3), and there was extensive desquamation. The patient died of candidemia after 14 days in ICU.
A 51-year-old woman with diabetes, who was mentally retarded and lived in a nursing home was hospitalized in an internal medicine ward on May 2017 with fever of no obvious source. She had no known exposure to dogs or ticks at the nursing home. The case-patient was hypotensive at admission, and laboratory results included a standard leukocyte count, thrombocytopenia (73,000 platelets/μL), hyponatremia, acute renal failure, increased levels of CK (1,933 IU/L) and liver enzymes, and a C-reactive protein level of 350 mg/L (Table 1). She was treated empirically with ceftriaxone.
On the third day of hospitalization, an infectious diseases consultation was performed, and intravenous doxycycline was added to the treatment regimen. She was transferred to the ICU unit, and the next day a maculopapular rash developed, which included the palms and soles; the rash rapidly became confluent and bullous, and skin necrosis followed.
PCR results for a whole blood sample and a skin biopsy specimen were positive for R. conorii subsp. israelensis. Serologic analysis on day 6 of the fever showed an IgM titer >1:100 and a borderline IgG titer of 1:100 for rickettsia.
Despite treatment with doxycycline, multiorgan failure developed and the patient died of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia related to central line infection 3 weeks after admission.
Three other case-patients were admitted to Laniado Hospital (Netanya, Israel) during April–May 2017 for fever and a maculopapular rash involving the palms that appeared on the third or fourth day after fever onset. Two patients had exposure to dogs, but none reported exposure to ticks. One patient had alcoholism, but he had a benign illness course. The diagnosis for 2 patients was made by using PCR for skin biopsy specimens, and the diagnosis for the third patient was made by using seroconversion. Skin biopsy PCR results were positive despite 3–4 days of doxycycline treatment.
Serologic Analysis
Serologic diagnosis was made by using indirect immunofluorescence assays. Serum samples were obtained from 5 patients and tested for antibodies against R. conorii and R. typhi as described (11).
DNA Extraction and PCR Detection
We extracted DNA from skin biopsy or whole blood specimens from 4 patients by using the QIAamp Mini Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. We tested samples for SFG rickettsiae by using nested PCR to amplify a fragment of the 17-kDa protein antigen gene as described (12). For further identification, we performed an additional PCR by using primers derived from consensus sequences of the rickettsial outer membrane protein A gene (213F 5′-AATCAATATTGGAGCCGGTAA-3′ and 667R 5′-ATTTGCATCAATCGTATAAGTAGC-3′). We analyzed sequences by using BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). This fragment was identical to that of the Israeli tick typhus rickettsial outer membrane protein A gene (GenBank accession no. U83441.1).
SFG rickettsial disease is endemic to Israel and might be related to deaths of infected patients. However, manifestation of ISF as primary purpura fulminans has been described only rarely. Thus, we report patients with rickettsial disease and purpura fulminans.
Among various species of SFG rickettsiae, the types known to be associated with patient deaths are R. rickettsii (agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever); R. conorii of the subtypes conorii, israelensis, and indica; and rarely R. australis (13). Although patient deaths are associated with vasculitis and multiorgan failure, purpura fulminans as part of the clinical presentation is a feature seen only for a small subset of the species, namely R. rickettsii, R. australis (14), and probably R. conorii subsp. indica. R. conorii subsp. indica was reported in several case series from the Indian subcontinent as a cause of fern-leaf pattern purpura, although the specific rickettsial subtype was infrequently identified in these studies (15–20).
Purpura fulminans is not a typical feature of ISF in reviews and in case series from Israel and other countries to which R. conorii subsp. israelensis is endemic (5,6,21). Although there are reports of deaths of patients in Israel who had a clinical picture suspected initially to be meningococcemia, fern-leaf purpura, as for 2 of our case-patients, was not part of the clinical descriptions (22). We have found only 1 case report of R. conorii subsp. israelensis infection and purpura fulminans (23). We report 2 additional cases.
The type of severe skin damage in the 2 case-patients we report is not the natural history of fatal spotted fever cases because it has not been described in other patients dying of ISF. The severe and confluent skin lesions undoubtedly contributed to bloodstream infections, leading to death in both cases. Because the differential diagnosis of purpura fulminans in Israel usually includes microorganisms other than rickettsiae, this deadly, unreported, unique, and potentially misleading manifestation of ISF must be recognized and treated in a timely fashion.
The clinical presentation of case-patients in this case series was typical of ISF and compatible with other case series of ISF (Table 2) (5,24). The reasons why 2 of these patients died and the other 3 patients had relatively mild disease is not entirely clear. Both case-patients who died were older; had hypotension, purpura fulminans, multiorgan failure, and acute renal failure; and showed increased levels of CK. Delay in doxycycline administration was evident for case-patient 1 (day 6 after illness onset) because she was hospitalized at a later time. A delay in doxycycline administration during medical observation occurred for case-patient 2, although treatment was given on day 5 after disease onset, which was similar to the timing for the 3 case-patients who survived.
We sequenced rickettsiae isolated from the 2 case-patients who died; both were positive for R. conorii subsp. israelensis. However, we did not perform sequencing for isolates from the other 2 case-patients who were positive by PCR for the SFG rickettsiae. These findings suggest that disease severity might be related to the specific subtype, and not to host factors, but further research is required. Alcoholism has been reported a risk factor for fatal disease (5), but the patient in this case series who had alcoholism had a benign course of illness.
With regards to epidemiologic, clinical, and laboratory findings, as expected, none of our patients had an eschar or known exposure to ticks. One patient had diarrhea, but 2 patients had constipation. All 5 case-patients had rash and laboratory abnormalities typical of ISF (Table 1), as described (24).
As previously reported (6,24), serologic analysis was not useful in the diagnosis of ISF because results were nonreactive for all case-patients early in the disease course and positive for 2 case-patients tested during the convalescent period (19 days after disease onset). In contrast, whole blood and skin biopsy specimen PCRs were helpful in obtaining a diagnosis. PCR results for skin biopsy specimens were positive for 4 of the 5 case-patients even though these PCRs were performed for 4 patients 3–4 days after doxycycline therapy was begun. The 1 case-patient with a negative PCR result for a skin biopsy specimen also had no inflammatory changes by histologic analysis, Thus, the negative PCR result for this patient probably represented a sampling error and not a false-negative result.
PCR for whole blood was performed for 2 patients: case-patient 2 showed a positive result after 3 days of doxycycline therapy, and case-patient 5 showed a negative result after 5 days of doxycycline therapy. Reduced sensitivity of whole blood PCR after beginning antimicrobial drug therapy has been reported (24). For the 4 case-patients with positive PCR results for skin biopsy specimens, the pathology report did not indicate a diagnosis of rickettsiosis, describing either intravascular coagulation and no vasculitis for the 2 patients who died and perivascular minimal lymphocytic infiltration not consistent with rickettsiosis for the other 2 patients.
Our cluster was a part of an outbreak throughout Israel during the spring and summer of 2017. This outbreak included deaths of 2 healthy young persons. One of these persons was a 15-year-old boy from the Sharon District. During July 2017, the Israeli Ministry of Health reported on an increased incidence of spotted fever cases (11 cases during January–May 2017); the yearly average is 6 cases (25).
In summary, during the spring and summer of 2017, there was an increased incidence of spotted fever in Israel, causing the deaths of 4 patients. Three of these patients acquired the disease in the Sharon District, and 2 were seen in our facility. Two of the case-patients who died were confirmed by sequencing to be infected with R. conorii subsp. israelensis; both of these patients had purpura fulminans and multiorgan failure. Purpura fulminans should increase the suspicion of ISF, along with other better-described pathogens, such as Neisseria meningitidis, and diagnostic and therapeutic measures must be taken urgently.
PCR of skin biopsy specimens is useful in providing a rapid and accurate diagnosis, even if performed 3–4 days after beginning of treatment, and PCR of whole blood might also show positive results during antimicrobial drug treatment early in the disease course. Histopathologic results for skin lesions might be inaccurate and cause a delay in diagnosis or an erroneous diagnosis. Features of R. conorii subsp. israelensis should be further explored primarily by performing genetic sequencing of all isolates from cases of spotted fever diagnosed in Israel to distinguish it from other spotted fever rickettsiae or R. conorii subsp. conorii that might cause a less aggressive disease.
Dr. Cohen is head of the Infectious Diseases Unit, Sanz Medical Center, Laniado Hospital, Netanya, Israel. His research interests are vectorborne diseases, zoonoses, and healthcare-associated infections.
Acknowledgment
References
- de Sousa R, Nóbrega SD, Bacellar F, Torgal J. Mediterranean spotted fever in Portugal: risk factors for fatal outcome in 105 hospitalized patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;990:285–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mumcuoglu KY, Keysary A, Gilead L. Mediterranean spotted fever in Israel: a tick-borne disease. Isr Med Assoc J. 2002;4:44–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Waner T, Keysary A, Eremeeva ME, Din AB, Mumcuoglu KY, King R, et al. Rickettsia africae and Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae in ticks in Israel. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014;90:920–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harrus S, Perlman-Avrahami A, Mumcuoglu KY, Morick D, Baneth G. Molecular detection of Rickettsia massiliae, Rickettsia sibirica mongolitimonae and Rickettsia conorii israelensis in ticks from Israel. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:176–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sousa R, França A, Dória Nòbrega S, Belo A, Amaro M, Abreu T, et al. Host- and microbe-related risk factors for and pathophysiology of fatal Rickettsia conorii infection in Portuguese patients. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:576–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colomba C, Trizzino M, Giammanco A, Bonura C, Di Bona D, Tolomeo M, et al. Israeli Spotted Fever in Sicily. Description of two cases and minireview. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;61:7–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chai JT, Eremeeva ME, Borland CD, Karas JA. Fatal Israeli spotted fever in a UK traveler to South Portugal. J Travel Med. 2008;15:122–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Znazen A, Hammami B, Lahiani D, Ben Jemaa M, Hammami A. Israeli spotted fever, Tunisia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1328–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maia C, Ferreira A, Nunes M, Vieira ML, Campino L, Cardoso L. Molecular detection of bacterial and parasitic pathogens in hard ticks from Portugal. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:409–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bechelli J, Smalley C, Milhano N, Walker DH, Fang R. Rickettsia massiliae and Rickettsia conorii Israeli spotted fever strain differentially regulate endothelial cell responses. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0138830. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Keysary A, Strenger C. Use of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques with cross-reacting human sera in diagnosis of murine typhus and spotted fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:1034–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Leitner M, Yitzhaki S, Rzotkiewicz S, Keysary A. Polymerase chain reaction-based diagnosis of Mediterranean spotted fever in serum and tissue samples. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:166–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parola P, Paddock CD, Socolovschi C, Labruna MB, Mediannikov O, Kernif T, et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: a geographic approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:657–702. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McBride WJ, Hanson JP, Miller R, Wenck D. Severe spotted fever group rickettsiosis, Australia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1742–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kundavaram A, Francis NR, Jude AP, Varghese GN. Acute infectious purpura fulminans due to probable spotted fever. J Postgrad Med. 2014;60:198–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weerakoon K, Kularatne SA, Rajapakse J, Adikari S, Waduge R. Cutaneous manifestations of spotted fever rickettsial infections in the Central Province of Sri Lanka: a descriptive study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3179. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Katoch S, Kallappa R, Shamanur MB, Gandhi S. Purpura fulminans secondary to rickettsial infections: A case series. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:24–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Luke N, Munasinghe H, Balasooriya L, Premaratna R. Widespread subcutaneous necrosis in spotted fever group Rickettsioses from the coastal belt of Sri Lanka- a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17:278. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tirumala S, Behera B, Jawalkar S, Mishra PK, Patalay PV, Ayyagari S, et al. Indian tick typhus presenting as Purpura fulminans. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2014;18:476–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Joshi HS, Thomas M, Warrier A, Kumar S. Gangrene in cases of spotted fever: a report of three cases. BMJ Case Rep. 2012 Dec 18;2012:pii:bcr2012007295.
- Keysary A, Potasman I, Itzhaki A, Finkelstein R, Yitzhaki S, Strenger C, et al. Clusters of Mediterranean spotted fever in Israel. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007;7:143–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yagupsky P, Wolach B. Fatal Israeli spotted fever in children. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17:850–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weinberger M, Keysary A, Sandbank J, Zaidenstein R, Itzhaki A, Strenger C, et al. Fatal Rickettsia conorii subsp. israelensis infection, Israel. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:821–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ergas D, Sthoeger ZM, Keysary A, Strenger C, Leitner M, Zimhony O. Early diagnosis of severe Mediterranean spotted fever cases by nested-PCR detecting spotted fever Rickettsiae 17-kD common antigen gene. Scand J Infect Dis. 2008;40:965–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Israel Center for Disease Control. Ministry of Health. Publication files, infectious diseases, notifiable infectious diseases in Israel, 2012 [cited 2018 Jan 19]. https://www.health.gov.il/English/News_and_Events/Spokespersons_Messages/Pages/05072017_2.aspx
Figures
Tables
Follow Up
Earning CME Credit
To obtain credit, you should first read the journal article. After reading the article, you should be able to answer the following, related, multiple-choice questions. To complete the questions (with a minimum 75% passing score) and earn continuing medical education (CME) credit, please go to http://www.medscape.org/journal/eid. Credit cannot be obtained for tests completed on paper, although you may use the worksheet below to keep a record of your answers.
You must be a registered user on http://www.medscape.org. If you are not registered on http://www.medscape.org, please click on the “Register” link on the right hand side of the website.
Only one answer is correct for each question. Once you successfully answer all post-test questions, you will be able to view and/or print your certificate. For questions regarding this activity, contact the accredited provider, CME@medscape.net. For technical assistance, contact CME@medscape.net. American Medical Association’s Physician’s Recognition Award (AMA PRA) credits are accepted in the US as evidence of participation in CME activities. For further information on this award, please go to https://www.ama-assn.org. The AMA has determined that physicians not licensed in the US who participate in this CME activity are eligible for AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™. Through agreements that the AMA has made with agencies in some countries, AMA PRA credit may be acceptable as evidence of participation in CME activities. If you are not licensed in the US, please complete the questions online, print the AMA PRA CME credit certificate, and present it to your national medical association for review.
Article Title:
Two Cases of Israeli Spotted Fever with Purpura Fulminans, Sharon District, Israel, 2016–2017
CME Questions
1. Which of the following subspecies of Rickettsia conorii is associated with the highest case fatality rate among humans?
A. R. conorii subsp. conorii
B. R. conorii subsp. caspia
C. R. conorii subsp. indica
D. R. conorii subsp. israelensis
2. Which of the following symptoms or complications is most likely to be part of the presentation of Israel spotted fever (ISF)?
A. Maculopapular rash involving the palms and soles
B. Endocarditis
C. Endophthalmitis
D. Purpura fulminans
3. Which of the following history or signs was most common among the 5 cases of ISF presented in the current study?
A. Known exposure to ticks
B. Transaminitis
C. A single eschar
D. Diarrhea
4. Which of the following tests was most helpful in the early identification of rickettsial disease in the current case series?
A. Serum immunoglobulin M for spotted fever group rickettsia
B. Serum immunoglobulin G for spotted fever group rickettsia
C. The presence of leukocytosis
D. Skin biopsy polymerase chain reaction tests
Original Publication Date: April 12, 2018
Related Links
Table of Contents – Volume 24, Number 5—May 2018
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Regev Cohen, Infectious Diseases Unit, Sanz Medical Center, Laniado Hospital, 16 Divrei Haim St, Kiryat Sanz, 42150, Netanya, Israel
Top