Volume 26, Number 10—October 2020
Dispatch
Emerging Sand Fly–Borne Phlebovirus in China
Figure 2
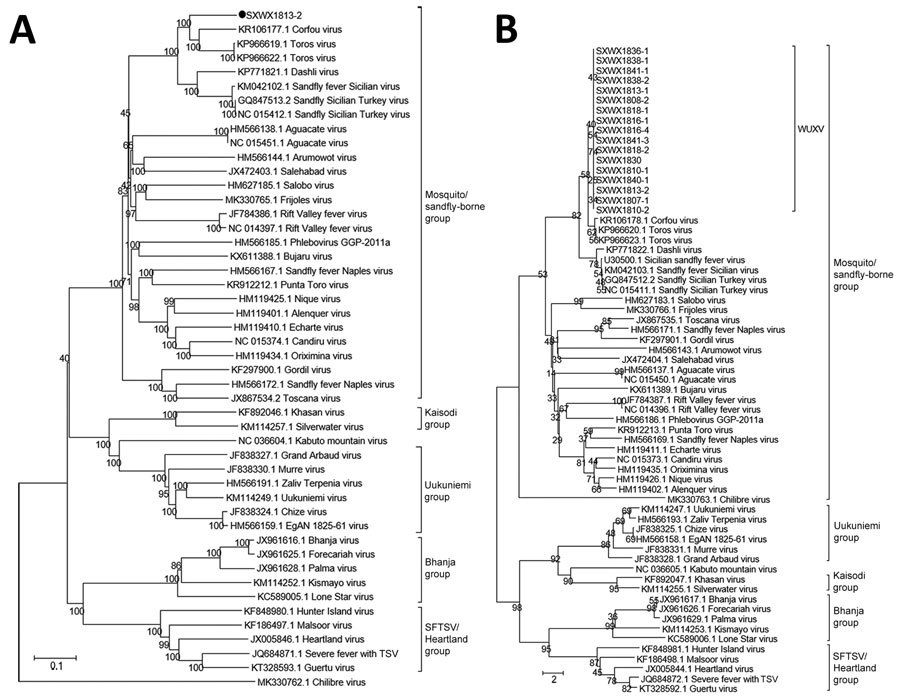
Figure 2. Evolution of nucleotide sequences of the large and medium gene segments of WUXV, a new phlebovirus isolated in China. A) Phylogenetic analysis of nucleotide sequences and molecular genetic evolution analysis of the large gene of WUXV isolate SXWX1813-2 (black dot), and reference isolates. B) Phylogenetic analysis of nucleotide sequences and molecular evolution analyses of the medium genes of 17 WUXV isolates, and reference isolates. MEGA 6.0 (https://www.megasoftware.net) and the neighbor-joining method were used for genetic evolution analysis with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. SFTSV, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus; WUXV, Wuxiang virus.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: June 30, 2020
Page updated: September 17, 2020
Page reviewed: September 17, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.