Volume 26, Number 10—October 2020
Research Letter
Rapid Screening Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assays Using Z-Scores to Standardize Results
Figure
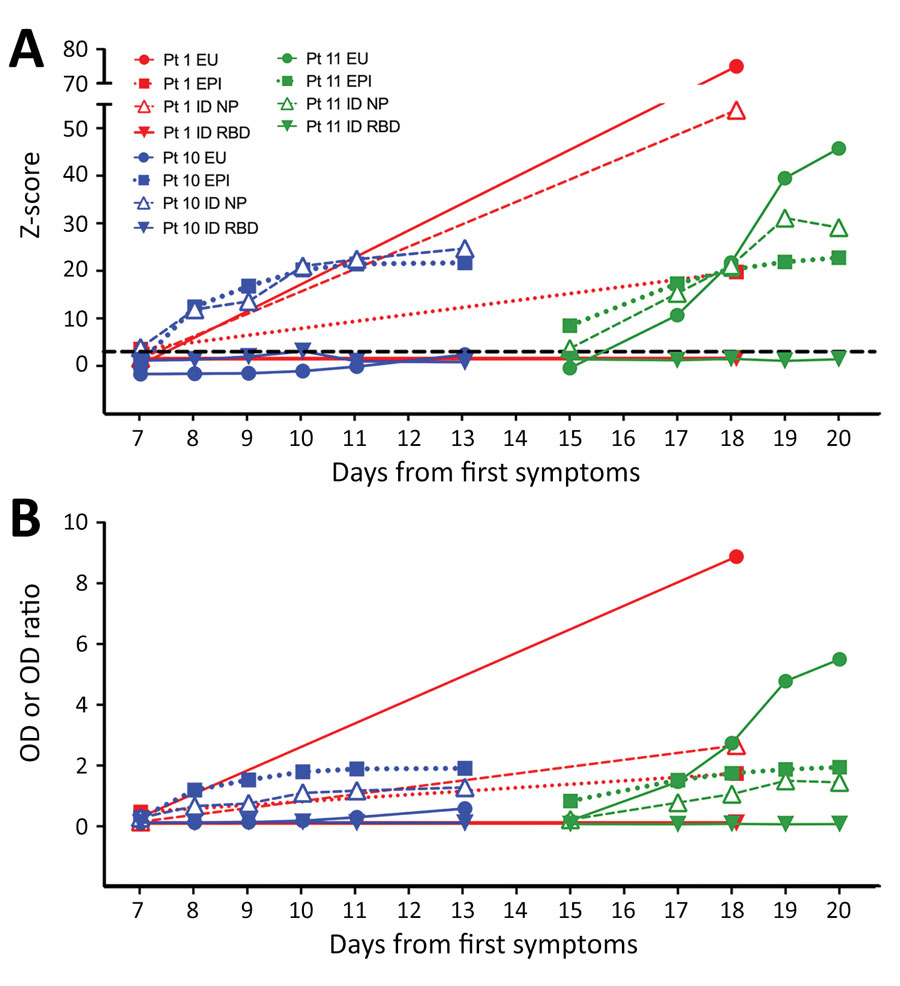
Figure. Results from 4 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 IgG assays, by days from first symptoms, for 3 patients with serial results demonstrating seroconversion. Immunoassay results are shown as z-scores (A), calculated from OD or OD ratio (EU) results (B) as described, and respective negative control population means and SDs for each assay (n = 25). Control samples were collected from healthy persons during 2015–2019 and tested with all 4 assays. For all patients, results from different assays are indicated as EU IgG (solid circles); EPI IgG (solid squares); ID NP IgG (open triangles); and ID S1RBD IgG (solid triangles). Red indicates results for patient 1, blue indicates results for patient 10, and green indicates results for patient 11. Dashed line in panel A indicates the z-score positivity threshold of 3. EPI, Epitope Diagnostics (http://www.epitopediagnostics.com); EU, Euroimmun (https://www.euroimmun.com); ID, ImmunoDiagnostics (https://www.immunodiagnostics.com.hk); NP, nucleocapsid protein; OD, optical density; RBD, receptor-binding domain; S, spike protein.