Volume 26, Number 11—November 2020
Dispatch
Epileptic Seizure after Use of Moxifloxacin in Man with Legionella longbeachae Pneumonia
Figure 1
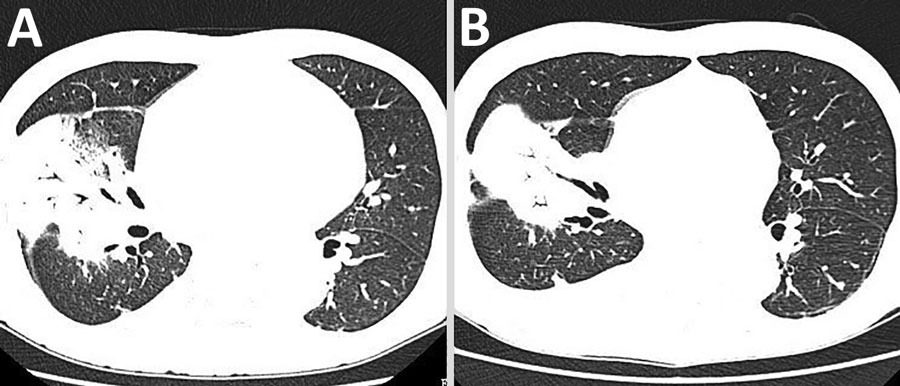
Figure 1. Computed tomographic scan of the chest of a patient hospitalized with Legionella longbeachae. A) On day 14 of the patient’s hospital stay, extensive consolidation was present in the right upper and middle lobe. B) On day 25 of the patient’s hospital stay, the consolidation was smaller than before.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: October 13, 2020
Page updated: October 19, 2020
Page reviewed: October 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.