Volume 26, Number 12—December 2020
Research
Equine-Like H3 Avian Influenza Viruses in Wild Birds, Chile
Figure 5
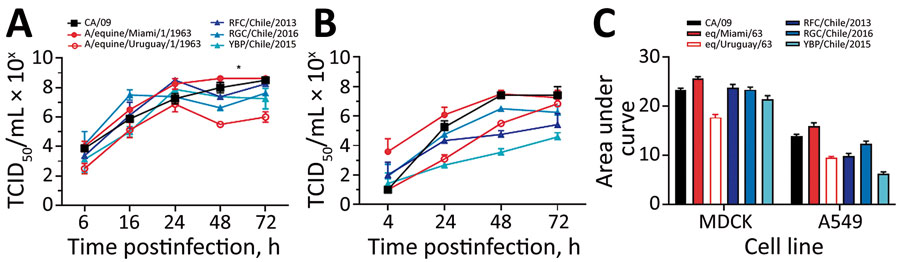
Figure 5. Replicative capacity of H3Nx influenza viruses in vitro. A, B) To evaluate the replication of H3N8 viruses in vitro, MDCK cells (A) and human lung A549 cells (B) were infected at a multiplicity of infection of 0.01, and cell culture supernatants were collected at 6, 16, 24, 48, and 72 hours postinfection. Viral titers were determined by TCID50 analysis in triplicate. Values are mean titers of 3 replicates, and error bars indicate SEMs. Differences were considered significant at p<0.05 (*). C) Cumulative shedding for each cell line and each viral strain shown. TCID50, 50% median tissue culture infectious dose.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 27, 2020
Page updated: November 19, 2020
Page reviewed: November 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.