Volume 26, Number 12—December 2020
Research Letter
Serologic Responses in Healthy Adult with SARS-CoV-2 Reinfection, Hong Kong, August 2020
Figure
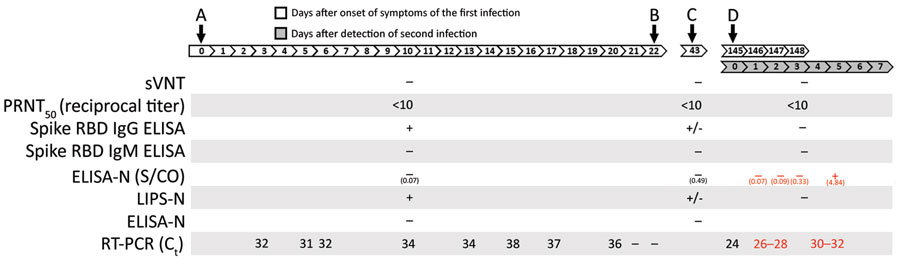
Figure. Timeline of primary infection and reinfection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Hong Kong, August, 2020. A) Onset. B) Discharge. C) Clinical follow-up. D) Mandatory testing. Black font indicates data from this investigation; red font indicates data from To et al. (6). Ct, cycle threshold; ELISA-N, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for N protein; LIPS, luciferase immune precipitation assay; PRNT50, 50% plaque reduction neutralization test titer; RBD, receptor binding domain; RT-PCR, reverse transcription PCR; S/CO, ratio of optical density readings of sample divided by cutoff (ratio of >1.4 considered positive); sVNT, surrogate virus neutralization test; +, positive; –, negative; +/–, borderline.
References
- Kiyuka PK, Agoti CN, Munywoki PK, Njeru R, Bett A, Otieno JR, et al. Human coronavirus NL63 molecular epidemiology and evolutionary patterns in rural coastal Kenya. J Infect Dis. 2018;217:1728–39. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Callow KA. Effect of specific humoral immunity and some non-specific factors on resistance of volunteers to respiratory coronavirus infection. J Hyg (Lond). 1985;95:173–89. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Perera RA, Mok CK, Tsang OT, Lv H, Ko RL, Wu NC, et al. Serological assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), March 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020;25:
2000421 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Hachim A, Kavian N, Cohen CA, Chin AWH, Chu DKW, Mok CKP, et al. ORF8 and ORF3b antibodies are accurate serological markers of early and late SARS-CoV-2 infection. [Erratum in: Nat Immunol. 2020 Aug 27; Epub ahead of print]. Nat Immunol. 2020 Aug 17 [Epub ahead of print].PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Addetia A, Crawford KHD, Dingens A, Zhu H, Roychoudhury P, Huang ML, et al. Neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection from SARS-CoV-2 in humans during a fishery vessel outbreak with high attack rate. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;Aug 21:
JCM.02107-20 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - To KK, Hung IF, Ip JD, Chu AW, Chan WM, Tam AR, et al. COVID-19 re-infection by a phylogenetically distinct SARS-coronavirus-2 strain confirmed by whole genome sequencing. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;
ciaa1275 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Tan CW, Chia WN, Qin X, Liu P, Chen MI, Tiu C, et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:1073–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li JY, Liao CH, Wang Q, Tan YJ, Luo R, Qiu Y, et al. The ORF6, ORF8 and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 inhibit type I interferon signaling pathway. Virus Res. 2020;286:
198074 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: September 18, 2020
Page updated: November 19, 2020
Page reviewed: November 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.