Volume 26, Number 6—June 2020
Research
Emergence of New Non–Clonal Group 258 High-Risk Clones among Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase–Producing K. pneumoniae Isolates, France
Figure 1
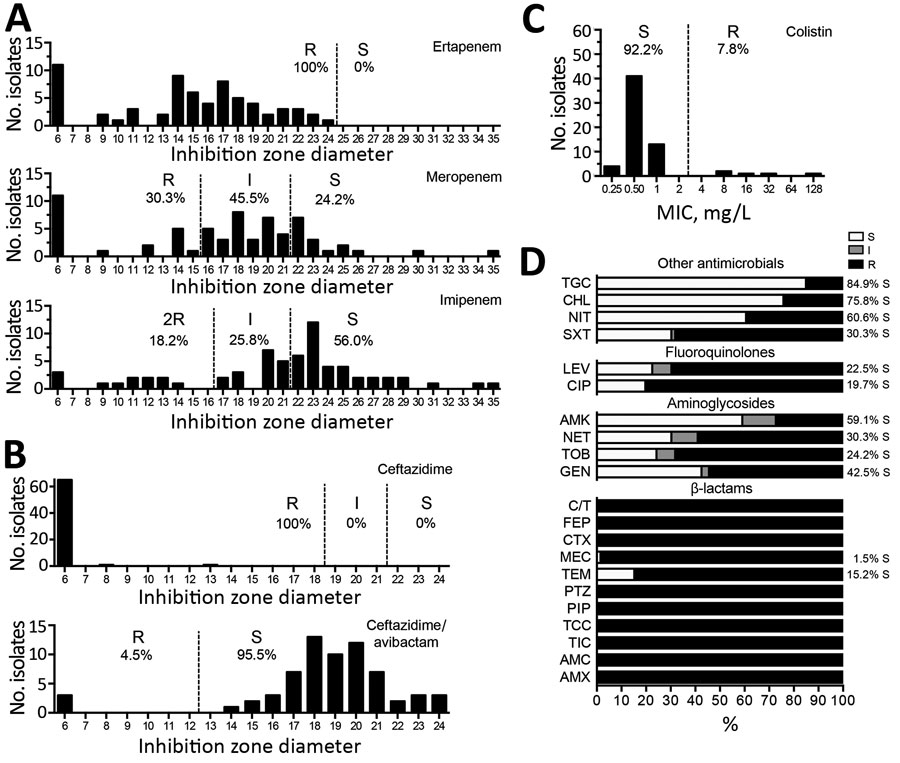
Figure 1. Susceptibility testing of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase–producing K. pneumoniae isolates, France, 2018. A) Antimicrobial susceptibility to carbapenems tested by using the disc diffusion method and interpreted according to European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing guidelines (http://www.eucast.org). B) Susceptibility to ceftazidime or ceftazidime/avibactam combination. C) MICs for colistin as determined by broth microdilution. D) Percentage of susceptibility to other antibiotic families. Where percentage of resistance is <100%, percentage of susceptible isolates is indicated. AMC, amoxicillin/clavulanate; AMK, amikacin; AMX, amoxicillin; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CHL, chloramphenicol; C/T, ceftolozane/tazobactam; CTX, cefotaxime; FEP, cefepime; GEN, gentamicin; I, intermediate; LEV, levofloxacin; MEC, mecillinam; NET, netilmicin; NIT, nitrofurane; PIP, piperacillin; PTZ, piperacillin/tazobactam; R, resistant; S, susceptible; TCC, ticarcillin/clavulanate; TEM, temocillin; TGC, tigecycline; TIC, ticarcillin.