Volume 27, Number 10—October 2021
Synopsis
Distribution and Characteristics of Human Plague Cases and Yersinia pestis Isolates from 4 Marmota Plague Foci, China, 1950–2019
Figure 1
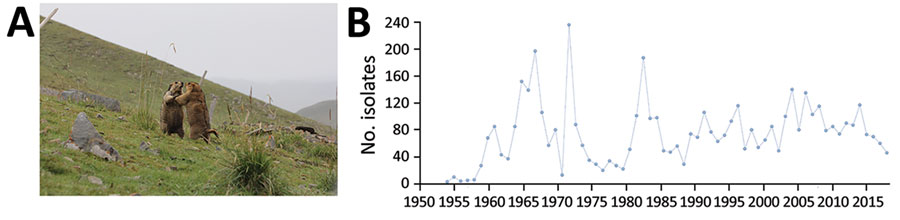
Figure 1. Plague ecology and surveillance of Yersinia pestis in the Marmota himalayana plague focus, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China, 1950–2019. This focus area encompasses Qinghai Province, Gansu Province, Tibet Autonomous Region, Sichuan Province, and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. A) The Himalayan marmot (M. himalayana), the predominant marmot species in this focus. Photograph by Xin Wang. B) Number of Y. pestis isolates collected from humans, animal hosts, and insect vectors (mostly Callopsylla dolabris and Oropsylla silantiewi fleas) in the focus.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 21, 2021
Page updated: October 13, 2021
Page reviewed: October 13, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.