Volume 27, Number 11—November 2021
Research
Genomic Profiling of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strains, Myanmar
Figure 4
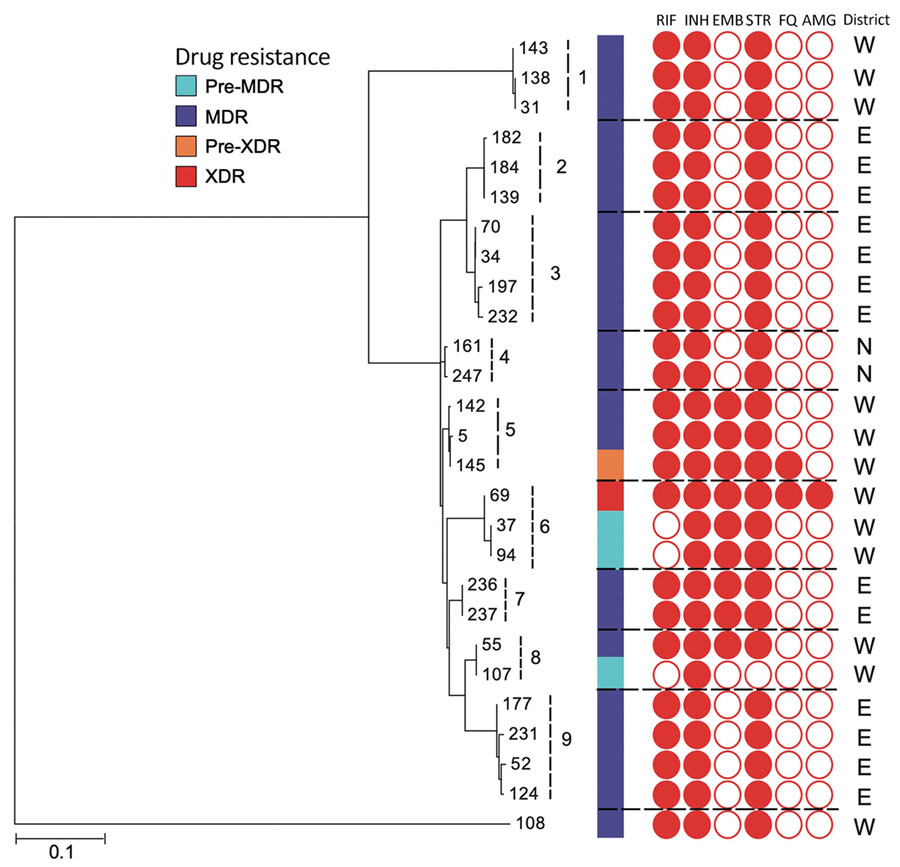
Figure 4. Maximum-likelihood tree of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains, Myanmar, within 9 clusters and their drug resistance profiles. Dotted lines indicate boundaries of individual clusters. An outgroup (#108) differs by >100 single-nucleotide polymorphisms from the strains within 9 clusters. N, E, and W indicate the North, East, and West Districts of Yangon, respectively. MDR, resistant to 2 first-line drugs (isoniazid and rifampin); pre-MDR, resistant to 1 of 2 first-line drugs (isoniazid or rifampicin); pre-XDR, resistant to fluoroquinolones or injectable drugs in addition to MDR; XDR, resistant to fluoroquinolones and injectable drugs, in addition to MDR. AMG, aminoglycosides; ETH, ethambutol; FQ, fluoroquinolones; INH, isoniazid; RIF, rifampin; STR, streptomycin. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.