Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 P.2 Lineage Associated with Reinfection Case, Brazil, June–October 2020
Paola Cristina Resende
, João Felipe Bezerra, Romero Henrique Teixeira Vasconcelos, Ighor Arantes, Luciana Appolinario, Ana Carolina Mendonça, Anna Carolina Paixao, Ana Carolina Duarte, Thauane Silva, Alice Sampaio Rocha, Ana Beatriz Machado Lima, Alex Pauvolid-Corrêa, Fernando Couto Motta, Dalane Loudal Florentino Teixeira, Thiago Franco de Oliveira Carneiro, Francisco Paulo Freire Neto, Isabel Diniz Herbster, Anderson Brandao Leite, Irina Nastassja Riediger, Maria do Carmo Debur, Felipe Gomes Naveca, Walquiria Almeida, Mirian Livorati, Gonzalo Bello
1, and Marilda M. Siqueira
1
Author affiliations: Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (P.C. Resende, I. Arantes, L. Appolinario, A.C. Mendonça, A.C. Paixao, A.C. Duarte, T. Silva, A.S. Rocha, A.B.M. Lima, A. Pauvolid-Corrêa, F.C. Motta, G. Bello, M.M. Siqueira); Universidade Federal da Paraíba, João Pessoa, Brazil (J.F. Bezerra, R.H.T. Vasconcelos); Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA (A. Pauvolid-Corrêa); Laboratório Central do Estado da Paraíba, João Pessoa (L.F. Teixeira, T.F. de Oliveira Carneiro); Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, Brazil (F.P.F. Neto); Maternidade Escola Januario Cicco, Natal (I.D. Herbster); Laboratório Central do Estado do Alagoas, Maceió, Brazil (A.B. Leite); Laboratório Central do Estado do Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil (I.N. Riediger, M.C. Debur); Instituto Leônidas e Maria Deane, on behalf of the COVIDNORTE team, Manaus, Brazil (F.G. Naveca); Ministério da Saúde do Brasil, Brasilia, Brazil (W. Almeida, M. Livorati)
Main Article
Figure 1
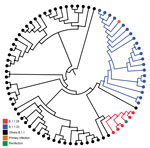
Figure 1. Maximum-likelihood tree of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 whole-genome sequences from Paraíba in study of reinfection case, Brazil, June–October 2020. Branching pattern of whole-genome sequences (29779 nt) from Paraíba (n = 77) are shown classified within lineages B.1.1.28 (red), B1.1.33 (blue), and others B.1.1 (black). Sequences derived from the primary infection and reinfection are highlighted with different colors as indicated. Nodes with high statistical support (approximate-likelihood ratio test >9.0) are marked by the smaller circular shapes.
Main Article
Page created: April 12, 2021
Page updated: June 16, 2021
Page reviewed: June 16, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
