Volume 29, Number 2—February 2023
Research
Penicillin and Cefotaxime Resistance of Quinolone-Resistant Neisseria meningitidis Clonal Complex 4821, Shanghai, China, 1965–2020
Figure 1
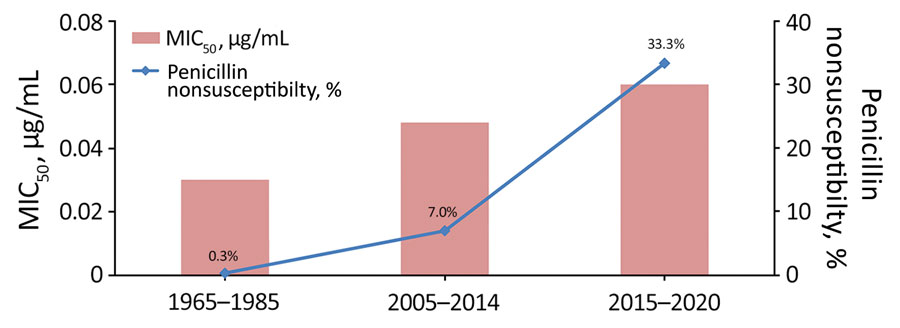
Figure 1. Percentage of meningococcal isolates with penicillin nonsusceptibility and MIC50 values, Shanghai, China, 1965–2020. MIC50, minimum inhibitory concentrations at which 50% of the tested isolates are inhibited.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: December 20, 2022
Page updated: January 21, 2023
Page reviewed: January 21, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.