Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Outbreak in New England Seals, United States
Wendy Puryear
1
, Kaitlin Sawatzki
1, Nichola Hill, Alexa Foss, Jonathon J. Stone, Lynda Doughty, Dominique Walk, Katie Gilbert, Maureen Murray, Elena Cox, Priya Patel, Zak Mertz, Stephanie Ellis, Jennifer Taylor, Deborah Fauquier, Ainsley Smith, Robert A. DiGiovanni, Adriana van de Guchte, Ana Silvia Gonzalez-Reiche, Zain Khalil, Harm van Bakel, Mia K. Torchetti, Kristina Lantz, Julianna B. Lenoch, and Jonathan Runstadler
Author affiliations: Tufts University Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine, North Grafton, Massachusetts, USA (W. Puryear, K. Sawatzki, A. Foss, J.J. Stone, M. Murray, E. Cox, J. Runstadler); University of Massachusetts, Boston, Massachusetts, USA (N. Hill); Marine Mammals of Maine, Brunswick, Maine, USA (L. Doughty, D. Walk, K. Gilbert); New England Wildlife Centers, Barnstable, Massachusetts, USA (P. Patel, Z. Mertz); New England Wildlife Centers, Weymouth, Massachusetts, USA (Z. Mertz); Wild Care, Inc., Eastham, Massachusetts, USA (S. Ellis, J. Taylor); National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Fisheries, Silver Spring, Maryland, USA (D. Fauquier); National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Fisheries, Gloucester, Massachusetts, USA (A. Smith); Atlantic Marine Conservation Society, Hampton Bays, New York, USA (R.A. DiGiovanni Jr.); Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine, New York, New York, USA (A. van de Guchte, A.S. Gonzalez-Reiche, Z. Khalil, H. van Bakel); US Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, Ames, Iowa, USA (M.K. Torchetti, K. Lantz); US Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA (J.B. Lenoch)
Main Article
Figure 2
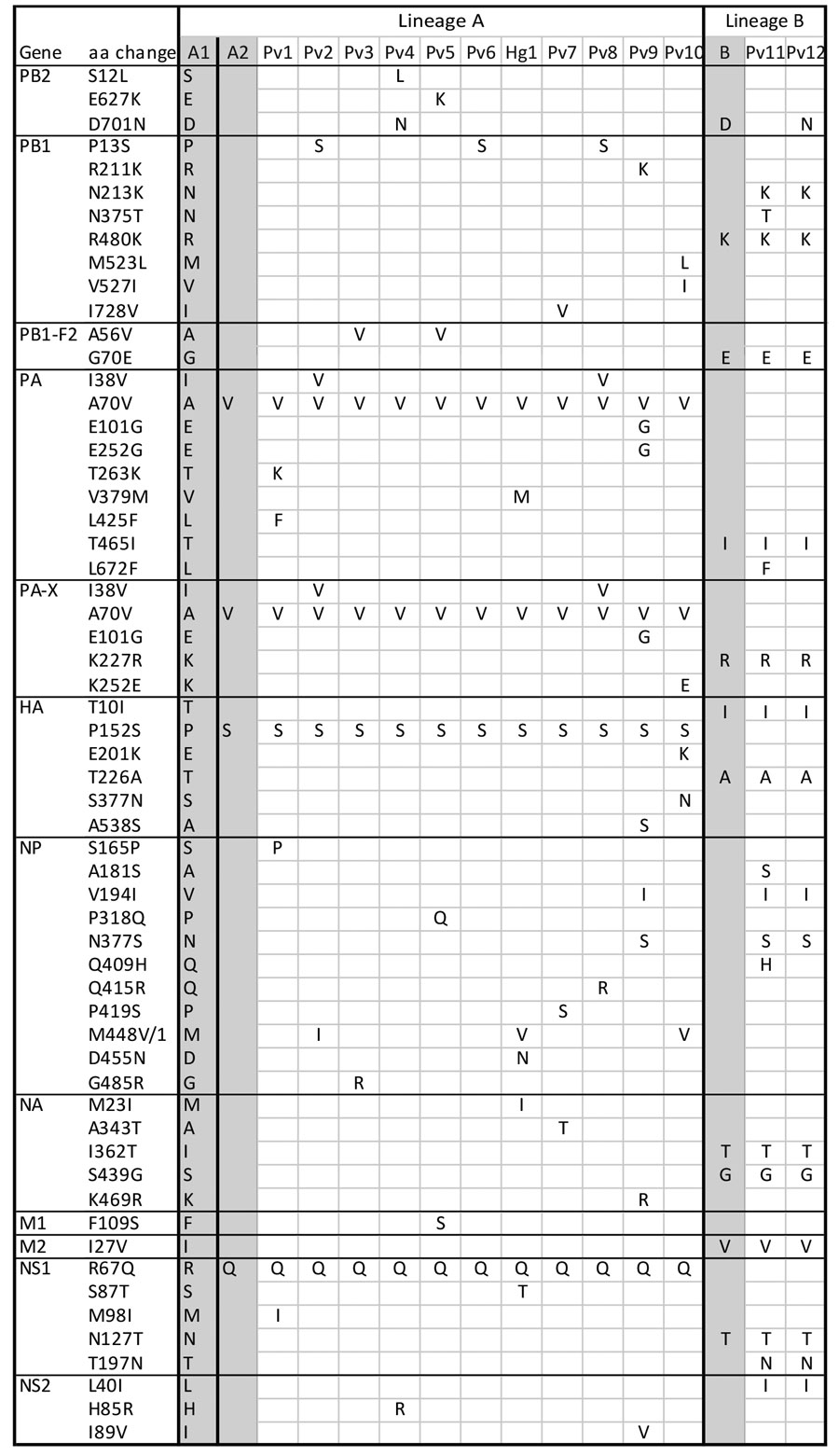
Figure 2. Amino acid changes in highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) viruses from New England birds and seals, United States. Each single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) that resulted in an amino acid change within ≥1 seal-derived sequence is shown. SNPs were observed in 12 H5N1 virus genes resulting in amino acid changes in corresponding proteins: PB2, PB1, PB1-F2, PA, PA-X, HA, NP, NA, M1, M2, NS1, and NS2. All avian virus reference sequences are shaded gray. A/Sanderling/MA/CW_22–112 (H5N1) (GISAID database, https://www.gisaid.org) (labeled A1) was used as a reference for first wave lineage A sequences; A/common eider/MA/TW_22–1400 (H5N1) (labeled A2) was used as a reference for second wave lineage A sequences; and A/common tern/MA/20220612_1 (H5N1) (labeled B) was used as a reference for lineage B sequences. Four aa differ between first and second wave lineage A viruses and 10 aa differ between first wave lineage A and lineage B. Second wave lineage A and lineage B seal-derived virus sequences, sampling date, and sampling location in Maine, USA, are indicated for each seal as follows: Pv1, MME22-112, 2022 Jun 22, Wells; Pv2, MME22-117, 2022 Jun 24, Yarmouth; Pv3, MME22-121, 2022 Jun 26, Georgetown; Pv4, MME22-122, 2022 Jun 27, New Harbor; Pv5, MME22-131, 2022 Jun 28, Harpswell; Pv6, MME22-133, 2022 Jun 29, S. Portland; Hg1, MME22-144, 2022 Jul 1, Phippsburg; Pv7, MME22-150, 2022 Jul 2, Westport; Pv8, MME22-155, 2022 Jul 2, Falmouth; Pv9, MME22-198, 2022 Jul 9, Wells; Pv10, MME22-230, 2022 Jul 15, Kennebunkport; Pv11, MME22-191, 2022 Jul 8, Harpswell; Pv12, MME22-195, 2022 Jul 9, Harpswell. HA, hemagglutinin; Hg, gray seal; M, matrix; NA, neuraminidase; NP, nucleoprotein; NS, nonstructural; PA, polymerase acidic; PB, polymerase basic; Pv, harbor seal.
Main Article
Page created: January 28, 2023
Page updated: March 21, 2023
Page reviewed: March 21, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
