Volume 6, Number 6—December 2000
Synopsis
Hemophagocytic Syndromes and Infection
Figure 2
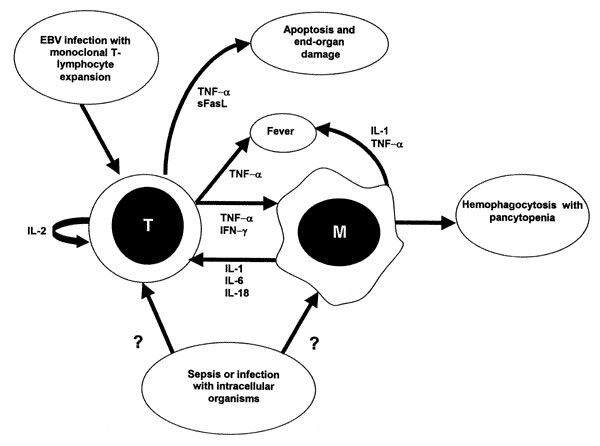
Figure 2. Schematic representation of possible immunopathologic mechanisms in infection-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). In Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated HLH, infection of T lymphocytes results in clonal proliferation, with production of high levels of activating cytokines. Elaboration of TNF-α and other cytokines causes fever and systemic illness. TNF-α and IFN-γ production contributes to macrophage activation with resulting hemophagocytosis, as demonstrated by the ability of anti-TNF-α and anti-IFN-γ antibodies to attenuate hemophagocytosis. The immunopathology of infection with nonviral pathogens is less well understood, but may be related to exaggerated production of TNF-α and IFN-γ in response to infection. TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ = interferon-gamma; IL-1 = interleukin-1; IL-2 = interleukin-2; IL-6 = interleukin-6; IL-18 = interleukin-18; sFasL = soluble Fas ligand; T = T-lymphocyte; M = macrophage; EBV = Epstein-Barr virus.