Volume 16, Number 10—October 2010
Dispatch
Emergence of Oseltamivir-Resistant Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Virus within 48 Hours
Figure
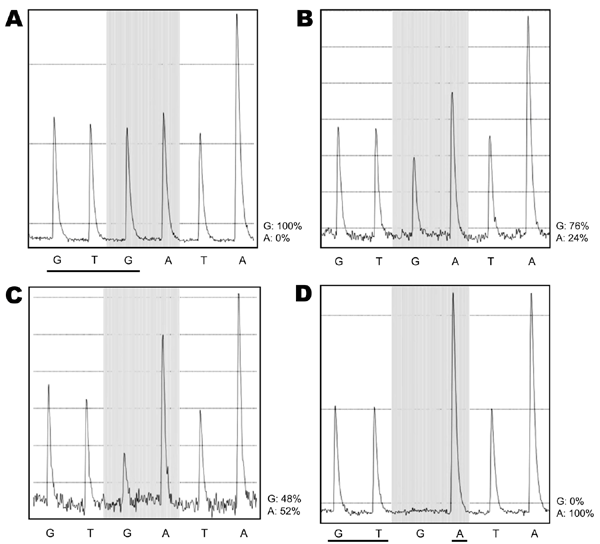
Figure. Pyrograms showing evolution of the H275Y mutation in pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus, Singapore. A) May 29, sample 14 h after receiving oseltamivir shows 100% G. B) May 30, 38-h sample shows 76% G and 24% A. C) May 30, sample at 45 h shows 48% G and 52% A. D) May 30, virus isolated from 38-h sample is 100% A. The shaded area indicates the mutation site, showing the progressive loss of the third base, G, and its replacement by A. In panel A, all bases have peaks of equivalent height because each base is a singlet, except for the last peak, which is double the height and represents an A followed by another A, as in AA. In panel D, the G at the mutation site has disappeared and the signal of the next base, A, has doubled in amplitude, indicating the complete replacement of G by A. This reflects replacement of the complementary base C by T in the viral template. The 3 bases that constitute aa 275 in the neuraminidase protein are underlined in panels A and D. In panel A, the sequence is 100% GTGATAA. In panel D, it is 100% GTAATAA. In panel A, the wild-type 5′-GTG-3′ is equivalent to 3′-CAC-5′ in its plus-strand RNA, which codes for histidine (H). Similarly, the mutant 5′-GTA-3′ in panel D is equivalent to 3′-CAT-5′, which codes for tyrosine (Y). Therefore, the pyrograms show a mutation from H to Y at position 275—the H275Y mutant.