Volume 9, Number 8—August 2003
Dispatch
NmcA Carbapenem-hydrolyzing Enzyme in Enterobacter cloacae in North America1
Figure 2
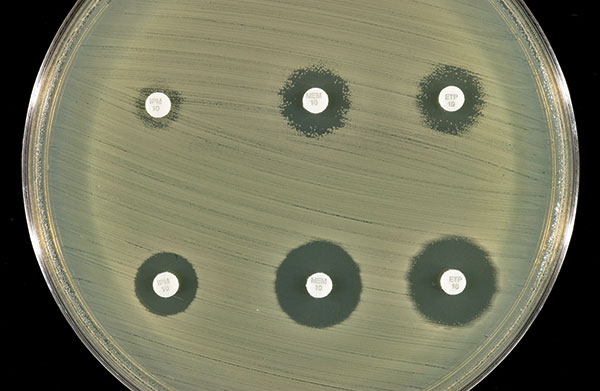
Figure 2. Effect of addition of clavulanic acid (10 μL of 1,000 μg/mL) to the zones of inhibition of the three carbapenem disks. Top row (left to right): imipenem, meropenem, and ertapenem disks without clavulanic acid. Bottom row (left to right): imipenem, meropenem, and ertapenem disks with clavulanic acid.
1This work was presented in part at the 13th Annual European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Glasgow, Scotland, 2003.
Page created: December 22, 2010
Page updated: December 22, 2010
Page reviewed: December 22, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.