Volume 21, Number 2—February 2015
Dispatch
Influenza D Virus in Cattle, France, 2011–2014
Figure
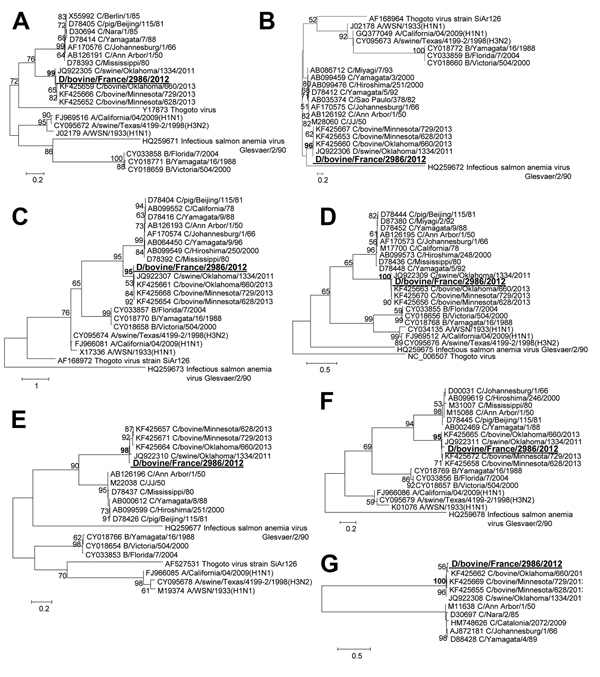
Figure. Phylogenetic trees of the 7 gene segments of D/bovine/France/2986/2012 influenza virus at the nucleotide level. A) PB2. B) PB1. C) P3/PA. D) Nucleoprotein E) P42/Matrix. F) Nonstructural protein. G) Hemagglutinin-esterase. Maximum-likelihood analysis with 500 bootstrap replicates (bootstrap values >75 are indicated on the tree nodes). The gene sequences of D/bovine/France/2986/2012 (in large bold underlined font) were compared with representatives of all the Orthomyxoviridae genera: all the viral strains used in (1). P, polymerase, nucleoprotein, PB, polymerase basic Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Hause BM, Collin EA, Liu R, Huang B, Sheng Z, Lu W, Characterization of a novel influenza virus in cattle and swine: proposal for a new genus in the Orthomyxoviridae family. MBio. 2014;5:e00031–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jiang WM, Wang SC, Peng C, Yu JM, Zhuang QY, Hou GY, . Identification of a potential novel type of influenza virus in Bovine in China. Virus Genes. 2014;49:493–6.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hause BM, Ducatez M, Collin EA, Ran Z, Liu R, Sheng Z, Isolation of a novel swine influenza virus from Oklahoma in 2011 which is distantly related to human influenza C viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003176. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kim JI, Park MS. N-linked glycosylation in the hemagglutinin of influenza A viruses. Yonsei Med J. 2012;53:886–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sun S, Wang Q, Zhao F, Chen W, Li Z. Glycosylation site alteration in the evolution of influenza A (H1N1) viruses. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e22844. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rosenthal PB, Zhang X, Formanowski F, Fitz W, Wong CH, Meier-Ewert H, Structure of the haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein of influenza C virus. Nature. 1998;396:92–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Webster RG, Bean WJ, Gorman OT, Chambers TM, Kawaoka Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol Rev. 1992;56:152–79 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sheng Z, Ran Z, Wang D, Hoppe AD, Simonson R, Chakravarty S, Genomic and evolutionary characterization of a novel influenza-C–like virus from swine. Arch Virol. 2014;159:249–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: January 21, 2015
Page updated: January 21, 2015
Page reviewed: January 21, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.