Travel- and Community-Based Transmission of Multidrug-Resistant Shigella sonnei Lineage among International Orthodox Jewish Communities
Kate S. Baker, Timothy J. Dallman, Adi Behar, François-Xavier Weill, Malika Gouali, Jeremy Sobel, Maria Fookes, Lea Valinsky, Ohad Gal-Mor, Thomas Connor, Israel Nissan, Sophie Bertrand, Julian Parkhill, Claire Jenkins, Dani Cohen, and Nicholas R. Thomson
Author affiliations: University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK (K.S. Baker); Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Hinxton, UK (K.S. Baker, M. Fookes, J. Parkhill, N.R. Thomson); Public Health England, London, UK (T.J. Dallman, C. Jenkins); Kimron Veterinary Institute, Bet Dagan, Israel (A. Behar); Institut Pasteur, Paris, France (F.X. Weill, M. Gouali); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (J. Sobel); Ministry of Health, Tel Aviv, Israel (L. Valinsky, I. Nissan); Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv (O. Gal-Mor, D. Cohen); Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK (T.R. Connor); Scientific Institute of Public Health, Brussels, Belgium (S. Bertrand); The London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London (N.R. Thomson)
Main Article
Figure 3
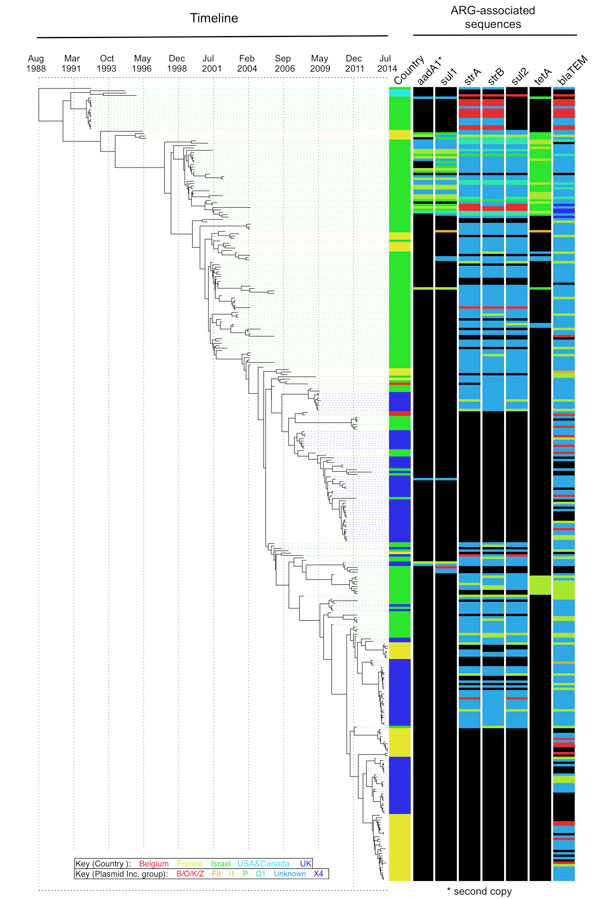
Figure 3.
The OJC-associated lineage of multidrug-resistant Shigella sonnei across time and associated antimicrobial drug resistance. The Bayesian-inferred phylogenetic tree shows the evolutionary relationships of 333 isolates (those for which a fixed date was available) in the OJC-associated lineage since its emergence in the late 1980s. Tree tips overlay the collection date of the isolates. Lane 1 at right shows the country of origin (colors shown in key), and subsequent tracks show the plasmid incompatibility groups (colors shown in key) of contiguous sequences carrying the named antimicrobial resistance genes in that isolate: lane 2, aadA1 (second copy); lane 3, sul1; lane 4, strA; lane 5, strB; lane 6, sul2; lane 7, tetA; lane 8, blaTEM. Black indicates gene not detected. The aadA1 genes described in this figure are in addition to the copy carried by all isolates in the OJC-associated lineage on the Tn7/Int2 cassette described in Results. OJCs, Orthodox Jewish communities.
Main Article
Page created: August 16, 2016
Page updated: August 16, 2016
Page reviewed: August 16, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
