Volume 24, Number 11—November 2018
Synopsis
Leishmaniasis in Northern Syria during Civil War
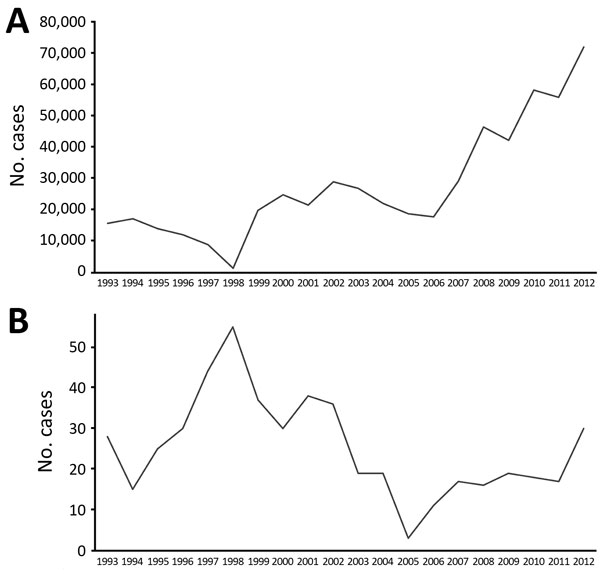
Figure 6
References
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory country views: Syrian Arab Republic, 1994–2010 [cited 2014 Aug 28]. http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/resources/SYRIAN_ARAB_REPUBLIC.pdf
- Salam N, Al-Shaqha WM, Azzi A. Leishmaniasis in the middle East: incidence and epidemiology. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3208. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hayani K, Dandashli A, Weisshaar E. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Syria: clinical features, current status and the effects of war. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:62–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alasaad S. War diseases revealed by the social media: massive leishmaniasis outbreak in the Syrian Spring. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Global strategic framework for integrated vector management; 2004 [cited 2017 Jan 2]. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/68624/WHO_CDS_CPE_PVC_2004_10.pdf?sequence=1
- Boggild AK, Miranda-Verastegui C, Espinosa D, Arevalo J, Adaui V, Tulliano G, et al. Evaluation of a microculture method for isolation of Leishmania parasites from cutaneous lesions of patients in Peru. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3680–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boggild AK, Miranda-Verastegui C, Espinosa D, Arevalo J, Martinez-Medina D, Llanos-Cuentas A, et al. Optimization of microculture and evaluation of miniculture for the isolation of Leishmania parasites from cutaneous lesions in Peru. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79:847–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Peruhype-Magalhães V, Machado-de-Assis TS, Rabello A. Use of the Kala-Azar Detect® and IT-LEISH® rapid tests for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012;107:951–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Valencia BM, Veland N, Alba M, Adaui V, Arevalo J, Low DE, et al. Non-invasive cytology brush PCR for the diagnosis and causative species identification of American cutaneous leishmaniasis in Peru. PLoS One. 2012;7:e49738. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boggild AK, Valencia BM, Espinosa D, Veland N, Ramos AP, Arevalo J, et al. Detection and species identification of Leishmania DNA from filter paper lesion impressions for patients with American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:e1–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- el Tai NO, Osman OF, el Fari M, Presber W, Schönian G. Genetic heterogeneity of ribosomal internal transcribed spacer in clinical samples of Leishmania donovani spotted on filter paper as revealed by single-strand conformation polymorphisms and sequencing. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2000;94:575–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schönian G, Nasereddin A, Dinse N, Schweynoch C, Schallig HD, Presber W, et al. PCR diagnosis and characterization of Leishmania in local and imported clinical samples. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003;47:349–58. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Haralambous C, Antoniou M, Pratlong F, Dedet JP, Soteriadou K. Development of a molecular assay specific for the Leishmania donovani complex that discriminates L. donovani/Leishmania infantum zymodemes: a useful tool for typing MON-1. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008;60:33–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hide M, Bañuls AL. Species-specific PCR assay for L. infantum/L. donovani discrimination. Acta Trop. 2006;100:241–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zackay A, Nasereddin A, Takele Y, Tadesse D, Hailu W, Hurissa Z, et al. Polymorphism in the HASPB repeat region of East African Leishmania donovani strains. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2031. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Van der Auwera G, Maes I, De Doncker S, Ravel C, Cnops L, Van Esbroeck M, et al. Heat-shock protein 70 gene sequencing for Leishmania species typing in European tropical infectious disease clinics. Euro Surveill. 2013;18:20543. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Number of cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis reported; data by country, 2005–2016 [cited 2018 June 22]. http://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.NTDLEISHCNUMv
- World Health Organization. Control of the leishmaniases. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2010; (
949 ):xii–xiii, 1–186, back cover.PubMedGoogle Scholar - Belazzoug S, Pratlong F, Rioux JA. [A new zymodeme of Leishmania tropica, agent of Aleppo boil (Syria)]. Arch Inst Pasteur Alger. 1988;56:95–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Al-Nahhas SA, Kaldas RM. Characterization of Leishmania species isolated from cutaneous human samples from central region of Syria by RFLP analysis. ISRN Parasitol. 2013;2013:308726. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Haddad N, Saliba H, Altawil A, Villinsky J, Al-Nahhas S. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in the central provinces of Hama and Edlib in Syria: Vector identification and parasite typing. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:524. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Khiami A, Dereure J, Pratlong F, Martini A, Rioux JA. La leishmaniose cutanée humaine à Leishmania major MON-26 aux environs de Damas (Syrie). Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 1991;84:340–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rioux J, Leger N, Haddad N, Desjeux P. Natural infestation of Phlebotomus tobbi (Diptera, Psychodidae) by Leishmania donovani s. st. (Kinetoplastida, Trypanosomatidae) in Syria. Parassitologia. 1998;40(Suppl1):148.
- Zackay A, Nasereddin A, Schnur L, Jaffe C. Molecular characterization of Leishmania donovani in Israel, GenBank accession no. HQ170543; 2016 [cited 2018 Jun 22]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/315454626/
- Alam MZ, Haralambous C, Kuhls K, Gouzelou E, Sgouras D, Soteriadou K, et al. The paraphyletic composition of Leishmania donovani zymodeme MON-37 revealed by multilocus microsatellite typing. Microbes Infect. 2009;11:707–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Antoniou M, Haralambous C, Mazeris A, Pratlong F, Dedet JP, Soteriadou K. Leishmania donovani leishmaniasis in Cyprus. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:6–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bhattacharyya T, Boelaert M, Miles MA. Comparison of visceral leishmaniasis diagnostic antigens in African and Asian Leishmania donovani reveals extensive diversity and region-specific polymorphisms. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2057. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gouzelou E, Haralambous C, Amro A, Mentis A, Pratlong F, Dedet JP, et al. Multilocus microsatellite typing (MLMT) of strains from Turkey and Cyprus reveals a novel monophyletic L. donovani sensu lato group. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:e1507. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Özbilgin A, Harman M, Karakuş M, Bart A, Töz S, Kurt Ö, et al. Leishmaniasis in Turkey: Visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania donovani in Turkey. Acta Trop. 2017;173:90–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kariyawasam UL, Selvapandiyan A, Rai K, Wani TH, Ahuja K, Beg MA, et al. Genetic diversity of Leishmania donovani that causes cutaneous leishmaniasis in Sri Lanka: a cross sectional study with regional comparisons. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17:791. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: October 16, 2018
Page updated: October 16, 2018
Page reviewed: October 16, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.