Volume 26, Number 12—December 2020
Dispatch
Experimental Infection of Cattle with SARS-CoV-2
Figure
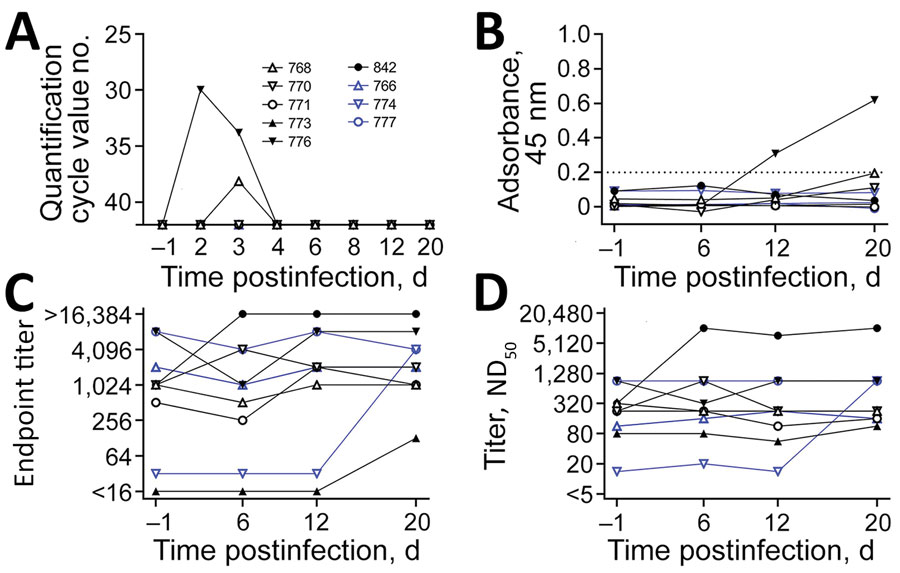
Figure. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 infection in cattle. Animals directly inoculated shown in black. In-contact animals shown in blue. Individual animals are indicated by the same symbol in every figure panel. A) Viral load in nasal swab samples measured by real-time RT-PCR. Animals 776 and 768 had detectable viral loads on days 2 and 3 (no. 776) or day 3 only (no. 768). B) Results of indirect ELISA specific to the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain. Serum samples taken on days −1 before infection and 6, 12, and 20 days after infection. Values below the dashed line are considered negative for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. C) Results of indirect immunofluorescence assay for BCoV. D) Results of virus neutralization test for BCoV. Indirect immunofluorescence and virus neutralization test showed that animal 842, which tested positive for BCoV in the nasal swab sample by real-time RT-PCR, had an increase in antibody titer against BCoV. Preinfection antibody titers against BCoV did not affect infection with SARS-CoV-2, as animals 776 and 768, which tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, showed no infection-related reaction of BCoV antibody titers. BCoV, bovine coronavirus; ND50, 50% neutralizing dose, RT-PCR, reverse transcription PCR; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.