Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Research
Naturally Acquired Human Plasmodium cynomolgi and P. knowlesi Infections, Malaysian Borneo
Figure 1
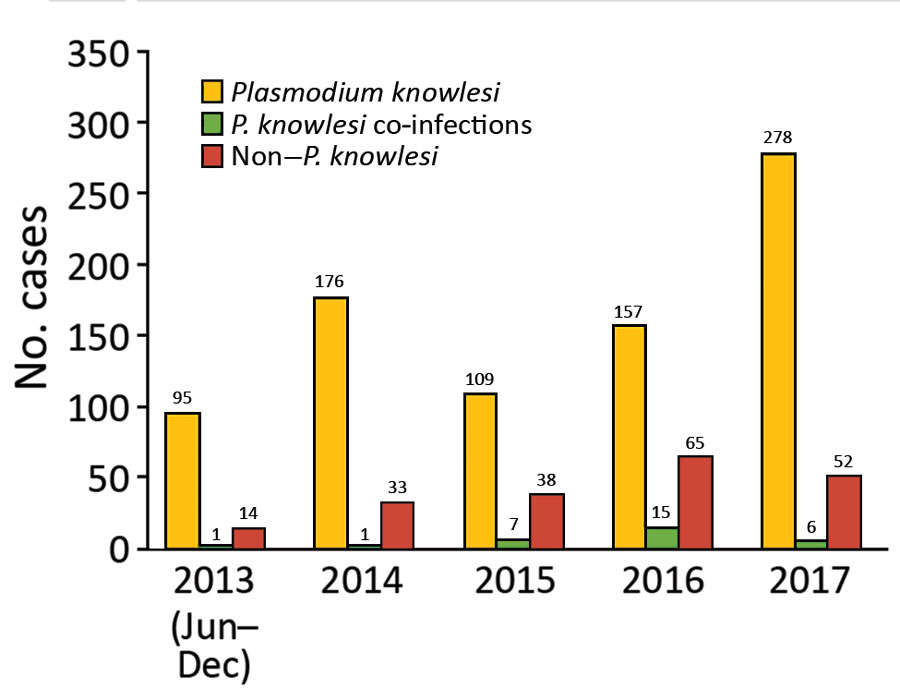
Figure 1. Number of patients admitted to Kapit Hospital with malaria during June 24, 2013–December 31, 2017, Malaysian Borneo. Non–P. knowlesi includes P. falciparum, P. malariae, P. ovale, and P. vivax. Infections with Plasmodium spp. other than P. knowlesi each year included the following. In 2013, P. knowlesi coinfections included 1 P. cynomolgi co-infection; non–P. knowlesi included 9 P. falciparum, 4 P. vivax, and 1 P. ovale. In 2014, P. knowlesi mixed included 1 P. falciparum coinfection; non–P. knowlesi included 14 P. falciparum, 4 P. malariae, 12 P. vivax, 3 P. ovale. In 2015, P. knowlesi co-infections included 3 P. falciparum and 4 P. vivax co-infections; non–P. knowlesi included 16 P. falciparum, 16 P. vivax, 1 P. malariae, 3 P. falciparum/P. vivax co-infections, 1 P. falciparum/P. ovale co-infection, and 1 P. vivax/P. ovale co-infection. In 2016, P. knowlesi co-infections included 8 P. falciparum, 6 P. vivax, and 1 P. cynomolgi co-infections; non–P. knowlesi included 41 P. falciparum, 14 P. vivax, 1 P. ovale, 3 P. falciparum/P. vivax co-infections, 1 P. falciparum/P. malariae co-infection, 4 P. falciparum/P. ovale co-infections, and 1 P. vivax/P. ovale co-infection. In 2017, P. knowlesi co-infections included 4 P. cynomolgi, and 2 P. vivax co-infections; non–P. knowlesi included 26 P. falciparum, 19 P. vivax, 3 P. malariae, 2 P. ovale, 1 P. falciparum/P. vivax co-infection, and 1 P. falciparum/P. malariae co-infection.