Volume 27, Number 6—June 2021
Research Letter
Incursion of Novel Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus, the Netherlands, October 2020
Figure
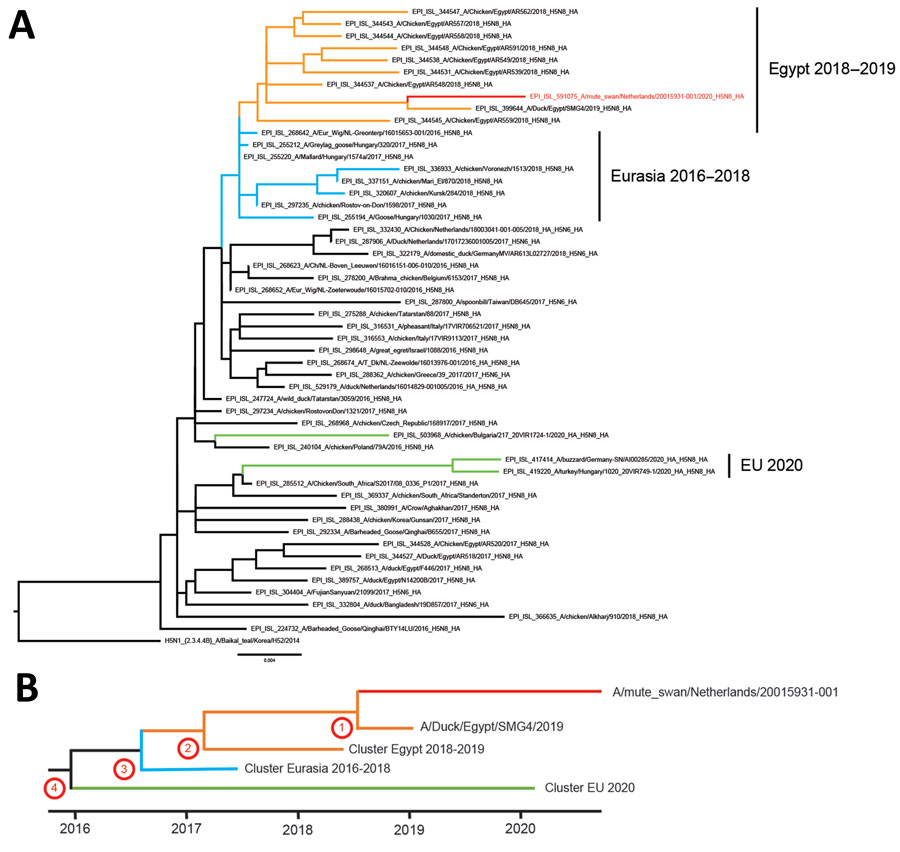
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of the hemagglutinin (HA) segment of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N8) virus, the Netherlands, October 2020. A) Optimal phylogenetic tree was generated by using the maximum-likelihood method (RAxML version 8.2.12; https://racm-ng.vital) with 100 bootstrap replicates and is shown and drawn to scale. GISAID (https://www.gisaid.org) accession numbers of the viruses are shown in the trees. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. B) Schematic representation of molecular dating of the HA gene segment. The Bayesian coalescent method was used to estimate the time to the most recent common ancestor of the novel H5N8 virus (numbers corresponding to nodes in the Table). Red branches indicate H5N8 virus isolated in the Netherlands in 2020;, green, H5N8 viruses isolated in eastern Europe, Germany, and Bulgaria in 2020; orange, viruses detected in Egypt during 2018–2019; and blue, viruses found in Eurasia during 2016–2018. EU, European Union.