Volume 27, Number 9—September 2021
Research
Human and Porcine Transmission of Clostridioides difficile Ribotype 078, Europe
Figure
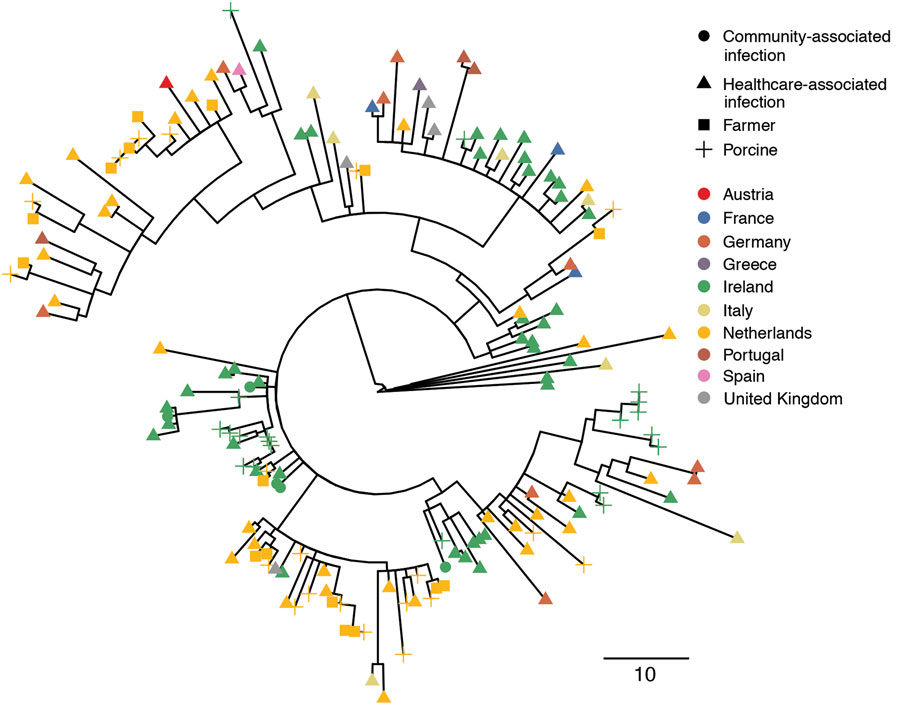
Figure. Recombination-adjusted maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of sequences from human and porcine Clostridioides difficile isolates from Ireland and 9 other countries in Europe. Isolates are shown as triangles for healthcare-associated C. difficile cases and circles for community-associated C. difficile cases. Isolates from pigs are shown as crosses and those from farmers as squares. The color at each tip indicates the country of origin of the isolate. The tree was based on 4,861 variable sites before correction for recombination, based on a median (interquartile ranges) of 93.4% (93.0%–93.8%) and (83.1%–96.2%) of the reference genome being called. Scale bar indicates single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.