Volume 29, Number 10—October 2023
Research
Ancestral Origin and Dissemination Dynamics of Reemerging Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae, Haiti
Figure 5
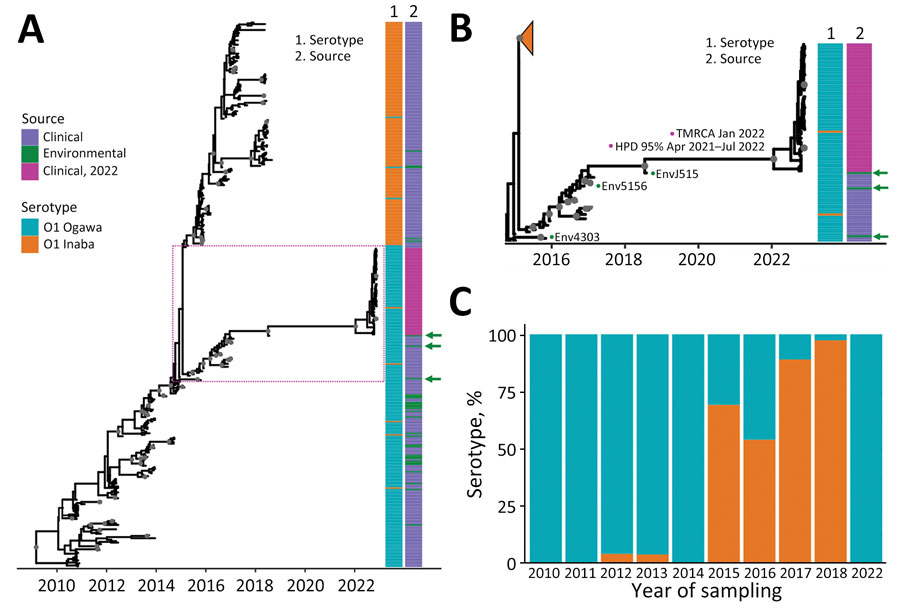
Figure 5. Inferred Bayesian phylogeny in a study of ancestral origin and dissemination dynamic of reemerging toxigenic Vibrio cholerae, Haiti. Phylogeny was inferred from 371 toxigenic V. cholerae O1 full genome clinical and environmental strains collected in Haiti during 2010–2022. A, B) Time-scaled phylogenies of V. cholerae serotypes inferred by enforcing a relaxed clock with Bayesian skyline demographic prior in BEAST version 1.10.4 (https://beast.community): A) Phylogeny of all isolates collected during 2010–2022. Dotted box denotes area detailed area shown in panel B. B) Detail of Ogawa clade from which the 2022 V. cholerae epidemic strains were derived. Gray circles indicate internal nodes supported by posterior probability >0.9. Branch lengths are scaled in time according to the x-axis. Time to MRCA of the 2022 Haiti isolates is shown at the node. Heatmaps denote clinical or environmental source and O1 serotype Ogawa or Inaba of the strains. Green arrows indicate the position of environmental strains basal to major clades. The collapsed orange clade refers to the monophyletic Inaba clade. Numbered green dots represent environmental V. cholerae O1 Ogawa isolates collected in Haiti; 2 were isolated from Jacmel Estuary, EnvJ515 in 2018 and Env4303 in 2015; Env5156 was isolated from a river in Leogane in 2016. C) Percentage of Ogawa and Inaba serotype isolates from samples collected in Haiti per year. HPD, high posterior density; MRCA, most recent common ancestor.
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.