Detection of Anopheles stephensi Mosquitoes by Molecular Surveillance, Kenya
Eric O. Ochomo
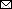
, Sylvia Milanoi, Bernard Abong’o, Brenda Onyango, Margaret Muchoki, Diana Omoke, Evelyn Olanga, Laban Njoroge, Elijah Omondi Juma, James Dan Otieno, Damaris Matoke-Muhia, Luna Kamau, Cristina Rafferty, John E. Gimnig, Mildred Shieshia, Daniel Wacira, Joseph Mwangangi, Marta Maia, Charles Chege, Ahmeddin Omar, Martin K. Rono, Lucy Abel, Wendy Prudhomme O’Meara, Andrew Obala, Charles Mbogo, and Lenson Kariuki
Author affiliations: Kenya Medical Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya (E.O. Ochomo, S. Milanoi, B. Abong’o, B. Onyango, M. Muchoki, D. Omoke, D. Matoke-Muhia, L. Kamau, J. Mwangangi, M. Maia, M.K. Rono, C. Mbogo); PMI Kinga Malaria Project, Abt Associates Inc., Kisumu, Kenya (E. Olanga); National Museums of Kenya, Nairobi (L. Njoroge); Pan-African Mosquito Control Association, Nairobi (E.O. Juma, D. Matoke-Muhia, C. Mbogo); World Health Organization, Kenya Country Office, Nairobi (J.D. Otieno); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, USA (C. Rafferty, J.E. Gimnig); US President’s Malaria Initiative, Washington, DC, USA (C. Rafferty, J.E. Gimnig, M. Shieshia, D. Wacira); University of Oxford, Oxford, UK (M. Maia); KEMRI-Wellcome Trust, Kilifi, Kenya (M. Maia, M.K. Rono); Division of National Malaria Program, Ministry of Health, Nairobi (C. Chege, A. Omar); Moi University, Eldoret (W.P. O’Meara, A. Obala); AMPATH, Eldoret, Kenya (L. Abel); Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, USA (W.P. O’Meara, L. Kariuki)
Main Article
Figure 5

Figure 5. Phylogeny of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 sequences of Anopheles stephensi mosquito isolates from Kenya (2023KEN0001, 2023KEN0002, and 2023KEN0003) and reference An. stephensi mosquito isolates retrieved from GenBank. GenBank accession numbers are provided for reference sequences; accession numbers for Kenya sequences are provided in [[ANCHOR###T3###Table 3###Anchor]]. Scale bar indicates 1% nucleotide sequence divergence. Values on the branches represent the percentage of 1,000 bootstrap replicates; bootstrap values >70% are shown in the tree.
Main Article
Page created: October 11, 2023
Page updated: November 18, 2023
Page reviewed: November 18, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
