Volume 29, Number 12—December 2023
Dispatch
Neurotropic Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus in Red Foxes, Northern Germany
Figure 2
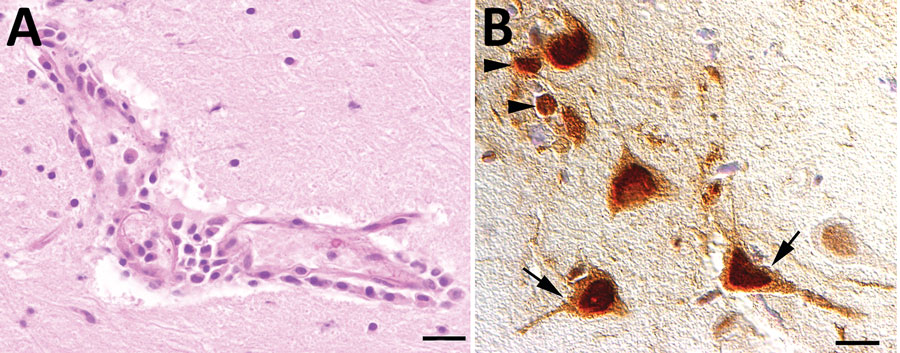
Figure 2. Results of testing for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes), Germany. A) Microscopic findings in the brain of an influenza A(H5N1) virus‒infected red fox showing a lymphocytic to histiocytic perivascular encephalitis (hematoxylin and eosin stained, scale bar = 50 μm). B) Immunohistochemical demonstration of influenza A virus nucleoprotein in neurons (arrows) and glial cells (arrowheads) in the cerebrum of a virus‒infected red fox (avidin biotin complex method, scale bar = 20 μm).
Page created: October 03, 2023
Page updated: November 18, 2023
Page reviewed: November 18, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.