Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Phylogeographic Analysis of Mycobacterium kansasii Isolates from Patients with M. kansasii Lung Disease in Industrialized City, Taiwan
Patrick George Tobias Cudahy, Po-Chen Liu, Joshua L. Warren, Benjamin Sobkowiak, Chongguang Yang, Thomas R. Ioerger, Chieh-Yin Wu, Po-Liang Lu, Jann-Yuan Wang, Hsiao-Han Chang, Hung-Ling Huang
, Ted Cohen, and Hsien-Ho Lin
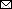
Author affiliations: Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, USA (P.G.T. Cudahy); National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan (P.-C. Liu, C.-Y. Wu, J.-Y. Wang, H.-H. Lin); Yale School of Public Health, New Haven (J.L. Warren, B. Sobkowiak, T. Cohen); Sun Yat-Sen University School of Public Health, Guangzhou, China (C. Yang); Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA (T.R. Ioerger); Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan (P.-L. Lu, H.-L. Huang); Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan (P.-L. Lu, H.-L. Huang); National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan (H.-H. Chang); Kaohsiung Municipal Ta-Tung Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan (H.-L. Huang)
Main Article
Figure 2
![Associations of environmental and clinical risk factors with genetic relatedness based on pair-level data using hierarchical Bayesian regression models in phylogeographic analysis of Mycobacterium kansasii isolates from patients with M. kansasii lung disease in industrialized city, Taiwan. A) Odds ratios for pairs of M. kansasii isolates to be in a genetic cluster (using the single-nucleotide polymorphism [SNP] cutoff of 45). An odds ratio of >1 suggests that the risk factor was associated with genetic clustering. B) Risk ratios for increase in SNP distance between pairs of isolates. A risk ratio of <1 suggests that the risk factor was associated with a shorter pairwise SNP distance. The 3 smaller water purification plants (Lingkou, Baolai, and Lujhu) were not considered in the analysis as they together only provided service to 6 participants.](/eid/images/24-0021-F2.jpg)
Figure 2. Associations of environmental and clinical risk factors with genetic relatedness based on pair-level data using hierarchical Bayesian regression models in phylogeographic analysis of Mycobacterium kansasii isolates from patients with M. kansasii lung disease in industrialized city, Taiwan. A) Odds ratios for pairs of M. kansasii isolates to be in a genetic cluster (using the single-nucleotide polymorphism [SNP] cutoff of 45). An odds ratio of >1 suggests that the risk factor was associated with genetic clustering. B) Risk ratios for increase in SNP distance between pairs of isolates. A risk ratio of <1 suggests that the risk factor was associated with a shorter pairwise SNP distance. The 3 smaller water purification plants (Lingkou, Baolai, and Lujhu) were not considered in the analysis as they together only provided service to 6 participants.
Main Article
Page created: June 18, 2024
Page updated: July 10, 2024
Page reviewed: July 10, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
![Associations of environmental and clinical risk factors with genetic relatedness based on pair-level data using hierarchical Bayesian regression models in phylogeographic analysis of Mycobacterium kansasii isolates from patients with M. kansasii lung disease in industrialized city, Taiwan. A) Odds ratios for pairs of M. kansasii isolates to be in a genetic cluster (using the single-nucleotide polymorphism [SNP] cutoff of 45). An odds ratio of >1 suggests that the risk factor was associated with genetic clustering. B) Risk ratios for increase in SNP distance between pairs of isolates. A risk ratio of <1 suggests that the risk factor was associated with a shorter pairwise SNP distance. The 3 smaller water purification plants (Lingkou, Baolai, and Lujhu) were not considered in the analysis as they together only provided service to 6 participants.](/eid/images/24-0021-F2.jpg)