Volume 20, Number 2—February 2014
Dispatch
Molecular Detection of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense in Humans, China
Figure 2
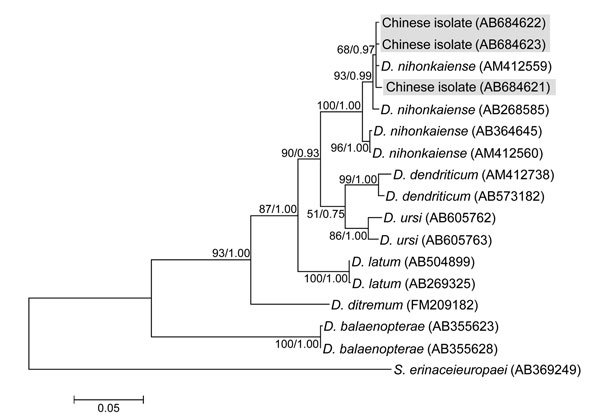
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree constructed by using the maximum likelihood algorithm (Kimura’s 2-parameter model) on the basis of the complete cox1 sequences of isolates from Diphyllobothrium species found in persons in China and related Diphyllobothrium speciesNumbers at nodes are bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) and posterior probabilities (106 generations) for maximum likelihood and Bayesian inference, respectivelySpirometra erinaceieuropaei was used as an outgroupScale bar indicates the number of base substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: January 16, 2014
Page updated: January 16, 2014
Page reviewed: January 16, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.