Volume 20, Number 2—February 2014
Dispatch
Fatal Systemic Morbillivirus Infection in Bottlenose Dolphin, Canary Islands, Spain
Abstract
A systemic morbillivirus infection was diagnosed postmortem in a juvenile bottlenose dolphin stranded in the eastern North Atlantic Ocean in 2005. Sequence analysis of a conserved fragment of the morbillivirus phosphoprotein gene indicated that the virus is closely related to dolphin morbillivirus recently reported in striped dolphins in the Mediterranean Sea.
Since the first morbillivirus outbreak affecting bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) along the mid-Atlantic Coast of the United States during the late 1980s (1), some mass die-off episodes affecting the global cetacean population have occurred (2–5). Three cetacean morbilliviruses have been identified: porpoise morbillivirus, isolated from harbor porpoises that died along the coast of Ireland (6); dolphin morbillivirus (DMV), first identified in striped dolphins from the Mediterranean Sea (2); and pilot whale morbillivirus, isolated from a long-finned pilot whale stranded in New Jersey, USA (7). Other members of the Paramyxoviridae family that have affected various marine mammal populations worldwide are phocine distemper virus and canine distemper virus (CDV) (8). Since early July 2013, a widespread die-off of >500 bottlenose dolphins occurred along the US mid-Atlantic Coast that probably resulted from morbillivirus infection (9).
We report a unique morbillivirus that caused documented systemic infection in a bottlenose dolphin from the eastern North Atlantic Ocean. Although this case occurred nearly 9 years ago, the nucleotide sequence of a fragment of the morbillivirus phosphoprotein (P) gene shows high homology with sequences recently reported for morbilliviruses from striped dolphins (Stenella coeruleoalba) in the Mediterranean Sea. This information is of value because no other sequences of morbillivirus from bottlenose dolphins are available in GenBank, despite the seriousness of this fatal disease, which causes mass deaths of marine mammals worldwide.
On July 18, 2005, a juvenile female bottlenose dolphin was stranded alive in Arrieta, Lanzarote (Canary Islands, Spain). The animal was 250 cm long and in moderate body condition, according to anatomic parameters. The animal died shortly after stranding, and a complete standardized necropsy was performed within 6 hours after death. Required permission for the management of stranded cetaceans in the Canarian archipelago is issued by the environmental department of the Canary Islands’ government.
Tissues of all the major organs and lesions were collected and stored in neutral buffered 10% formalin fixative solution for histologic and immunohistochemical analyses. Fixed tissue samples were trimmed and then routinely processed, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 5 μm, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for examination by light microscopy. A monoclonal antibody against the nucleoprotein of CDV (MoAb CDV-NP, VMRD, Inc., Pullman, WA, USA) known to react with DMV was used as primary antiserum. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed on selected samples of brain, intestinal, lymphatic, pancreatic, pulmonary, renal, and splenic tissues, as described (4). Samples of lung, spleen, and brain were collected and held frozen at −80°C until processed for molecular virology.
On gross examination, the most remarkable findings were moderate to severe multiorgan parasitic infection, mainly cirripedes (Xenobalanus sp.) in the caudal fin; larval cestodes (Phyllobothrium sp. and Monorygma grimaldi) within the subcutaneous and peritoneum tissues; nematodes (Anisakis spp.), trematodes (Pholeter sp.), and taeniform cestodes in the stomachs and intestine, and trematodes (Nasitrema sp.) and nematodes (Crassicauda sp.) within both pterygoid sinuses; bilateral serous-suppurative and proliferative arthritis at the scapula-humeral junction; and generalized lymphadenomegalia. Within the brain; the leptomeninges were enlarged and fibrotic at the cortex area.
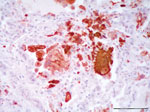
Histologically, the lesions were consistent with findings from the gross examination. Other histopathologic findings were multifocal nonsuppurative hepatitis, adrenalitis, and bronchointerstitial pneumonia. In lung, a multifocal suppurative bronchitis associated with larval and adult nematode parasites (morphologically identified as Halocercus spp. and Stenurus spp.) were observed. Alveolar septa were expanded by macrophages and lymphocytes admixed with scattered karyorrhectic debris. Alveoli were often lined by hyperplastic type II pneumocytes and filled with large numbers of multinucleated syncytial cells. The immunohistochemical study demonstrated morbilliviral antigen in bronchiolar epithelium, type 2 pneumocytes, and multinucleate (syncytial) cells from lung (Figure 1).
The syncytia also were found within the lymph nodes, pancreas, spleen, kidney, and intestine, and they were characterized by a moderate amount of eosinophilic cytoplasm and 2 to >20 nuclei, often containing weak stained eosinophilic inclusion bodies. Lymphocytolysis was remarkable within the spleen and multiple lymph nodes and were characterized by loss of cellular detail and accumulation of karyorrhectic and eosinophilic cellular debris. Syncytia from lymph nodes, spleen, pancreas, and kidney also were immunostained against CDV antibody. Severe nonsuppurative meningitis (with >20 layers of lymphohistiocytic cells), perineuritis, and encephalomyelitis were found within the nervous system. Multiple microhemorrhages were a common associated lesion. The brain showed severe inflammatory changes, but only a few neurons were immunopositive, and they were limited to some lymphohistiocytic cells surrounding vessels, glial, and endothelial cells. The epithelial tropism of the virus was demonstrated immunohistochemically within the lung, intestine, kidney, and pancreatic duct epithelium.
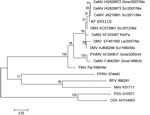
Molecular detection of cetacean morbillivirus was performed by a 1-step reverse transcription PCR of a 426-bp conserved region of the P gene, as described (10). All the samples tested from this dolphin were reverse transcription PCR positive for morbillivirus. Sequences were the same in all positive samples from the animal. We conducted a BLAST (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi) search to compare sequenced products with sequences described in GenBank for morbillivirus. The common sequence of 411-nt fragment of the P gene showed a 99% homology with those sequences obtained in 2007 and 2011 from striped dolphins stranded along the coastline of the Mediterranean Sea.
We used MEGA 5.0 software (www.megasoftware.net) to construct maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees. A bootstrap resampling (1,000 replicates) was used to assess the reliability of the trees (Figure 2).
We describe a systemic morbillivirus infection in a bottlenose dolphin in the Canary Islands. A previous morbillivirus infection had been described in a bottlenose dolphin found dead along the Atlantic coast of Mauritania in 1998; the virus was exclusively detected by hybridization in the stomach tissue sample (11).
Other cases that illustrate the systemic and neurologic features of the disease have been described in bottlenose dolphins in the Mediterranean Sea (12–14), and the first reported case of a fatal morbillivirus infection in cetaceans within the Southern Hemisphere (southwestern Pacific Ocean) has been described (15). No sequences from these studies were provided to GenBank, although the phylogenetic analyses showed high homology with other DMV. The P gene fragment of the virus obtained from the current study is molecularly almost identical to that reported in striped dolphins in the Mediterranean Sea during the last 5 years. This fact supports the hypothesis that transmission occurs between species, as it was reported in the 2006–2007 Mediterranean epizootic between pilot whales (Globicephala melas and G. macrorhynchus) and striped dolphins (3), and demonstrates that dolphin populations of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean are in contact through the Gibraltar Straits. This particular point is critical to better understand the epidemiology and transmission of morbilliviruses between cetaceans and could be essential to clarifying the infection source of the die-off of bottlenose dolphins alson the East Coast of the United States (9).
Dr Sierra is a researcher at the Institute for Animal Health at the University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. Her areas of expertise include veterinary pathology (including whale and dolphin pathology) and pathogenesis of animal infectious diseases, and her research interests include muscular pathologies on whales and dolphins.
Acknowledgments
We thank the other members of the Canary Islands Cetacean Stranding Network, SECAC (Society for the Study of the Cetaceans in the Canarian Archipelago), and Canarias Conservación.
This study was possible thanks to the partial funding by National Project CGL2012-39681 (Subprograma BOS); Regional Project SolSub C200801000288, and ProID 20100091; and Technical Assistant Contract by Canary Islands Government delegation (TEC0002955).
References
- Lipscomb TP, Schulman FY, Moffett D, Kennedy S. Morbilliviral disease in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from the 1987–1988 epizootic. J Wildl Dis. 1994;30:567–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Domingo M, Visa J, Pumarola M, Marco AJ, Ferrer L, Rabanal R, Pathologic and immunocytochemical studies of morbillivirus infection in striped dolphins (Stenella coeruleoalba). Vet Pathol. 1992;29:1–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fernández A, Esperón F, Herraéz P, de Los Monteros AE, Clavel C, Bernabé A, Morbillivirus and pilot whale deaths, Mediterranean Sea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:792–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raga JA, Banyard A, Domingo M, Corteyn M, Van Bressem MF, Fernandez M, Dolphin morbillivirus epizootic resurgence, Mediterranean Sea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:471–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rubio-Guerri C, Melero M, Esperon F, Belliere EN, Arbelo M, Crespo JL, Unusual striped dolphin mass mortality episode related to cetacean morbillivirus in the Spanish Mediterranean Sea. BMC Vet Res. 2013;9:106. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barrett T, Visser IK, Mamaev L, Goatley L, van Bressem MF, Osterhaust AD. Dolphin and porpoise morbilliviruses are genetically distinct from phocine distemper virus. Virology. 1993;193:1010–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taubenberger JK, Tsai MM, Atkin TJ, Fanning TG, Krafft AE, Moeller RB, Molecular genetic evidence of a novel morbillivirus in a long-finned pilot whale (Globicephalus melas). Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6:42–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kennedy S. Morbillivirus infections in aquatic mammals. J Comp Pathol. 1998;119:201–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. What’s causing the bottlenose dolphin deaths along the mid-Atlantic? [cited 2013 Sep 20]. http://www.nero.noaa.gov/stories/2013/bottlenosedolphinannouncement.html
- Reidarson TH, McBain J, House C, King DP, Stott JL, Krafft A, Morbillivirus infection in stranded common dolphins from the Pacific Ocean. J Wildl Dis. 1998;34:771–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van de Bildt MW, Martina BE, Sidi BA, Osterhaus AD. Morbillivirus infection in a bottlenosed dolphin and a Mediterranean monk seal from the Atlantic coast of West Africa. Vet Rec. 2001;148:210–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tsur I, Yakobson B, Elad D, Moffett D, Kennedy S. Morbillivirus infection in a bottlenose dolphin from the Mediterranean Sea. European Journal of Veterinary Pathology. 1997;2:83–5.
- Keck N, Kwiatek O, Dhermain F, Dupraz F, Boulet H, Danes C, Resurgence of morbillivirus infection in Mediterranean dolphins off the French coast. Vet Rec. 2010;166:654–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Di Guardo G, Di Francesco CE, Eleni C, Cocumelli C, Scholl F, Casalone C, Morbillivirus infection in cetaceans stranded along the Italian coastline: pathological, immunohistochemical and biomolecular findings. Res Vet Sci. 2013;94:132–7 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stone BM, Blyde DJ, Saliki JT, Blas-Machado U, Bingham J, Hyatt A, Fatal cetacean morbillivirus infection in an Australian offshore bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). Aust Vet J. 2011;89:452–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figures
Cite This ArticleTable of Contents – Volume 20, Number 2—February 2014
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Eva Sierra, Institute for Animal Health, Veterinary School, University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Canary Islands, SpainEva Sierra, Institute for Animal Health, Veterinary School, University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Canary Islands, Spain
Top