Volume 21, Number 11—November 2015
Dispatch
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome in 3 Persons, South Korea, 2015
Figure 1
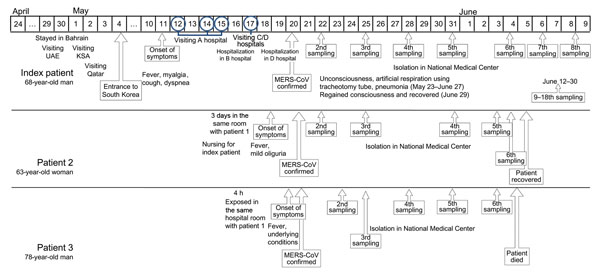
Figure 1. Timeline of events for patients infected with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). The laboratory diagnostic methods used for molecular detection of MERS-CoV RNA were multiplex MERS-CoV real-time reverse transcription PCRs targeting an upstream MERS-CoV envelope protein gene and an open reading frame 1a gene (8,9). KSA, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; UAE, United Arab Emirates.
References
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Frouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1814–20 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Emergencies preparedness, response: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) maps and epicurves. 10–16 August 2015 [cited 2015 Aug 20]. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/coronavirus_infections/maps-epicurves/en
- Korea Society of Infectious Diseases, Korean Society for Healthcare-associated Infection Control and Prevention. An unexpected outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in the Republic of Korea, 2015. Infect Chemother. 2015;47:120–2.
- Cowling BJ, Park M, Fang VJ, Wu P, Leung GM, Wu JT. Preliminary epidemiological assessment of MERS-CoV outbreak in South Korea, May to June 2015. Euro Surveill. 2015;20:21163 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee SS, Wong NS. Probable transmission chains of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus and the multiple generations of secondary infection in South Korea. Int J Infect Dis. 2015;38:65–7 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MERS countermeasure guideline (revised December 2014) [in Korean]. Cheongju (South Korea): The Centers; 2014.
- World Health Organization. Laboratory testing for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Interim recommendations (revised). September 2014. Geneva: The Organization; 2014.
- Corman VM, Eckerle I, Bleicker T, Zaki A, Landt O, Eschbach-Bludau M, Detection of a novel human coronavirus by real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Euro Surveill. 2012;17:20285 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Corman VM, Muller MA, Costabel U, Timm J, Binger T, Meyer B, Assays for laboratory confirmation of novel human coronavirus (hCoV-EMC) infections. Euro Surveill. 2012;17:pii20334 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:1312–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Spanakis N, Tsiodras S, Haagmans BL, Raj VS, Pontikis K, Koutsoukou A, Virological and serological analysis of a recent Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection case on a triple combination antiviral regimen. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014;44:528–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drosten C, Seilmaier M, Corman VM, Hartmann W, Scheible G, Sack S, Clinical features and virological analysis of a case of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:745–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Poissy J, Goffard A, Parmentier-Decrucq E, Favory R, Kauv M, Kipnis E, Kinetics and pattern of viral excretion in biological specimens of two MERS-CoV cases. J Clin Virol. 2014;61:275–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: October 19, 2015
Page updated: October 19, 2015
Page reviewed: October 19, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.