Volume 30, Number 1—January 2024
Dispatch
Helicobacter fennelliae Localization to Diffuse Areas of Human Intestine, Japan
Figure 1
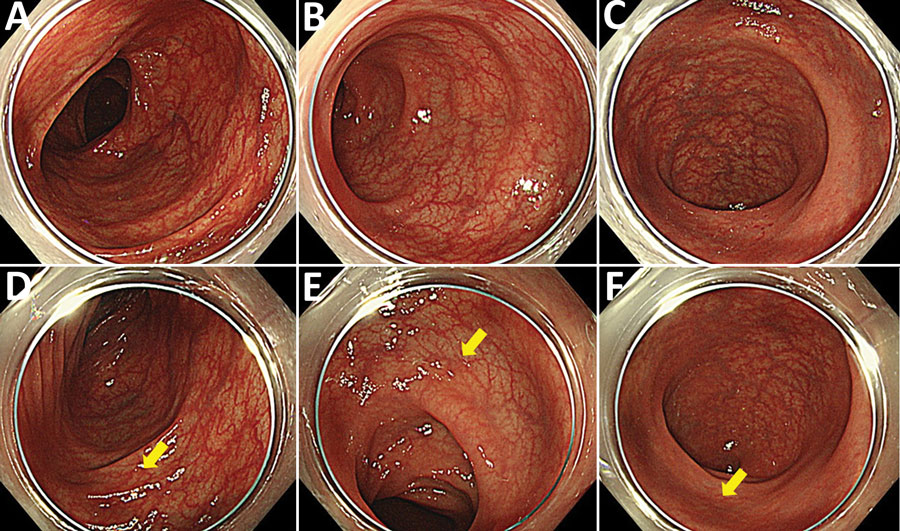
Figure 1. Colonoscopy findings from a man in Japan who had recurrent Helicobacter fennelliae bacteremia. A–C) First colonoscopy findings in the transverse colon (A), in the sigmoid colon (B), and in the rectum (C). D–F) Second colonoscopy findingsin the transverse colon (D), in the sigmoid colon (E), and in the rectum (F). Yellow arrows indicate randomly biopsied sites. Colonic vascular permeability was preserved, and there were no significant findings for inflammation.
Page created: November 30, 2023
Page updated: December 20, 2023
Page reviewed: December 20, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.