Volume 5, Number 6—December 1999
Dispatch
New Rickettsiae in Ticks Collected in Territories of the Former Soviet Union
Figure 2
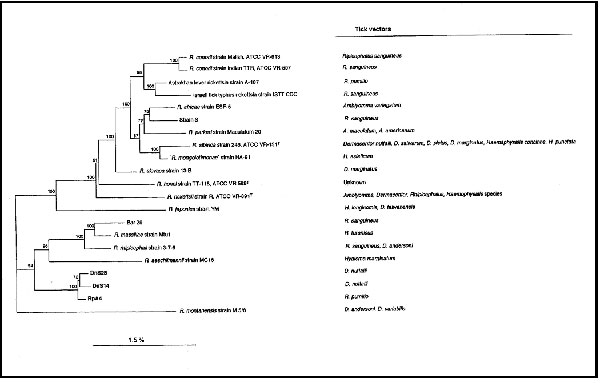
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree of Rickettsiae inferred from comparison of the ompA sequences. The known tick vectors for the bacteria presented on the dendrogram are indicated on the right. The ompA sequences were aligned by the multisequence alignment program CLUSTAL in the BISANCE software package. Phylogenetic relationships were inferred by using version 3.4 of the PHYLIP software package. Evolutionary distance matrices, generated by DNADIST, were determined by the Kimura method. Matrices were used to construct dendrograms by the neighbor-joining method. Data were also examined by using parsimony analysis (DNAPARS in PHYLIP), and bootstrap analyses were performed to investigate the stability of the trees obtained. Bootstrap values were obtained for a consensus tree based on 100 randomly generated trees by using SEQBOOT and CONSENSE in the same package. The percentage of similarity between strains was determined by using the PC/GENE software package.
1The received sequences of the new rickettsial agents have been deposited in GenBank. Sequences of ompA were deposited as two parts under accession numbers: DnS28, AF120018 and AF120019; DnS14, AF120021, and AF120020; RpA4, AF120022, and AF120023. The 16S rRNA gene and gltA sequences have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers DnS28, gltA - AF120027, 16S rRNA gene AF120024; DnS14, gltA AF120028, 16S rRNA gene AF120025; RpA4, gltA - AF120029, 16S rRNA gene AF120026.