Fatal Human Neurologic Infection Caused by Pigeon Avian Paramyxovirus-1, Australia
Siobhan Hurley
1
, John Sebastian Eden
1, John Bingham, Michael Rodriguez, Matthew J. Neave, Alexandra Johnson, Annaleise R. Howard-Jones, Jen Kok, Antoinette Anazodo, Brendan McMullan, David T. Williams, James Watson, Annalisa Solinas, Ki Wook Kim
2, and William Rawlinson
2
Author affiliations: Prince of Wales Hospital, Randwick, New South Wales, Australia (S. Hurley, K.W. Kim); Westmead Institute for Medical Research Centre for Virus Research, Westmead, New South Wales, Australia (J.S. Eden); Sydney Institute for Infectious Diseases, University of Sydney Faculty of Medicine and Health, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia (J.S. Eden, A.R. Howard-Jones); CSIRO Australian Centre for Disease Preparedness, Geelong, Victoria, Australia (J. Bingham, M.J. Neave, D.T. Williams, J. Watson); Prince of Wales and Sydney Children’s Hospital, Randwick (M. Rodriguez, A. Solinas); Sydney Children’s Hospital, Randwick (A. Johnson, B. McMullan); Centre for Infectious Diseases and Microbiology Laboratory Services, New South Wales Health Pathology–Institute of Clinical Pathology and Medical Research, Westmead (A.R. Howard-Jones, J. Kok); Kids Cancer Centre, Sydney Children’s Hospital, Randwick (A. Anazodo); University of New South Wales Faculty of Medicine and Health, School of Clinical Medicine, Sydney (B. McMullan, K. Kim); Prince of Wales Hospital and Community Health Services, Sydney (W. Rawlinson); University of New South Wales Schools of Clinical Medicine, Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, Sydney (W. Rawlinson)
Main Article
Figure 3
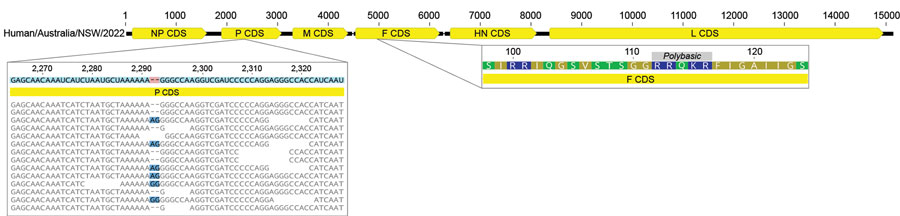
Figure 3. Genomic markers of virulence in avian paramyxovirus type 1 strain in an immunocompromised child in Australia. An analysis of both P and F genes indicated the strain would likely be classified as virulent based on P-gene editing; possible alternate reading frames were detected in mapped sequence reads (left side of panel). The F gene protein sequence carries a polybasic cleavage site at amino acid positions 112–116 (region on right of panel). CDS, coding sequences; F, fusion protein; G, glycoprotein; HN, hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein; L, large protein; M, matrix protein; NP, nucleoprotein; P, polymerase-associated phosphoprotein.
Main Article
Page created: November 13, 2023
Page updated: November 18, 2023
Page reviewed: November 18, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
