Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Research
Population Genomic Structure and Recent Evolution of Plasmodium knowlesi, Peninsular Malaysia
Figure 7
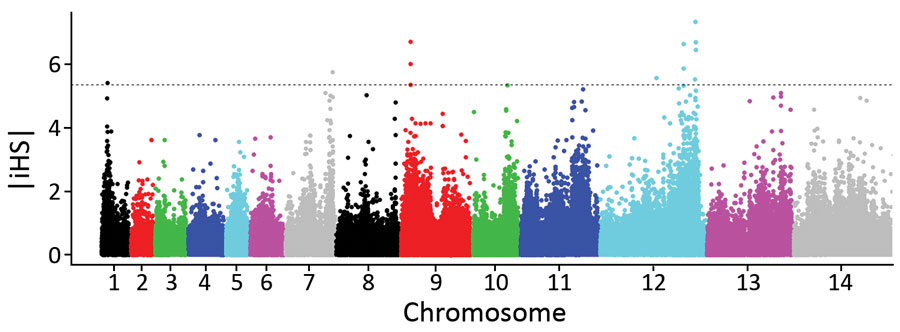
Figure 7. Scan for evidence of genomic regions affected by recent positive directional selection in Plasmodium knowlesi in Peninsular Malaysia, using the standardized integrated haplotype score |iHS| index. Examination of the ranges of extended haplotype homozygosity for individual single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with high |iHS| values identified 4 distinct genomic windows of extended haplotypes (Appendix 2 Datasheet 3). Two of these (in chromosomes 1 and 9) spanned across SICAvar and kir genes, which were masked from SNP calling, whereas the other 2 did not include SICAvar or kir genes but covered ≈28 kb on chromosome 7 and ≈315 kb on chromosome 12. The large region on chromosome 12 is a merged window, consisting of 4 high |iHS| core SNPs with overlapping windows of extended haplotype homozygosity, and coincides with the region of chromosome 12 that has the highest genomic divergence between cluster 3 population subclusters A and B (Figure 5, panel D).